What Is A Scraping Bot and How to Build One

Emma Foster
Machine Learning Engineer
15-Jan-2026
TL;Dr: Key Takeaways for Building Your Scraping Bot
- Scraping bots are advanced, automated programs that mimic human browsing to extract structured data at scale, unlike simpler, single-page scraping scripts.
- Modern bots require sophisticated tools like Playwright or Scrapy-Playwright to handle JavaScript and dynamic content effectively.
- Security measures (rate limiting, CAPTCHA, fingerprinting) are the biggest challenge; overcoming them requires proxies, request throttling, and specialized CAPTCHA solvers.
- Ethical and legal compliance is non-negotiable; always respect
robots.txtand the website's terms of service to avoid legal issues. - Differentiation in 2026 lies in integrating AI/LLMs for smarter data parsing and using robust, cloud-based infrastructure for continuous, large-scale operation.
Introduction
Data is the lifeblood of modern business, and the ability to collect it efficiently determines competitive advantage. This guide will show you exactly what is a scraping bot and how to build one that is robust, scalable, and compliant with modern web standards. A well-designed scraping bot is an essential tool for web scraping at scale, transforming raw web pages into actionable, structured datasets. This comprehensive tutorial is for developers, data scientists, and business analysts looking to master automated data extraction from the internet. We will cover everything from core definitions and technology stacks to the crucial security navigation techniques needed for success in 2026.
What Is a Scraping Bot?
A scraping bot is an autonomous software application designed to navigate websites and extract specific, structured data. These programs are more complex than simple scripts, as they are built to operate continuously, handle complex website structures, and often mimic human behavior to avoid detection. The core function of a scraping bot is to automate the repetitive task of gathering information, allowing for data collection that is both faster and more consistent than any manual process.
Core Definition and How It Works
A scraping bot operates by sending HTTP requests to a target website, receiving the HTML content, and then parsing that content to locate and extract the desired data points. The key difference from a basic script is the bot's ability to maintain state, manage sessions, and interact with dynamic elements.
The process generally follows these steps:
- Request: The bot sends a request to a URL, often using a rotating proxy to mask its true IP address.
- Rendering: For modern, JavaScript-heavy sites, the bot uses a headless browser (like Playwright or Puppeteer) to render the page, executing all necessary client-side code.
- Parsing: The bot uses a parsing library (like BeautifulSoup or lxml) to navigate the Document Object Model (DOM) and identify target data using CSS selectors or XPath.
- Extraction: The identified data is extracted, cleaned, and transformed into a structured format (e.g., JSON, CSV).
- Storage: The final data is stored in a database or file system for later analysis.
Types of Scraping Bots
Not all scraping bots are created equal; their design depends heavily on the target website's complexity and the required scale of operation.
| Bot Type | Description | Best Use Case | Key Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Script | Executes a single request and parses static HTML. Not a true "bot." | Small, static websites with no JavaScript. | requests, BeautifulSoup |
| Browser Automation Bot | Uses a headless browser to render JavaScript and simulate human interaction. | Dynamic websites, single-page applications (SPAs), login required. | Selenium, Puppeteer, Playwright |
| Distributed Bot | A network of bots running across multiple machines or cloud functions, managed by a central orchestrator. | Large-scale, high-volume web scraping projects requiring speed. | Scrapy, Kubernetes, Cloud Functions |
| AI-Enhanced Bot | Integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) to intelligently parse unstructured data or resolve complex security challenges. | Extracting data from highly variable or unstructured text content. | LLM APIs, Model Context Protocol (MCP) |
Key Stats on Scraping Bots
The use of scraping bots is a massive and growing industry, driven by the demand for real-time market intelligence. According to recent industry reports, the global web scraping market is projected to reach over $10 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 15% Grand View Research: Web Scraping Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. Furthermore, a significant portion of all internet traffic—estimated at over 40%—is non-human, with a large percentage attributed to legitimate and sophisticated bots, including search engine crawlers and commercial scraping bots. This data underscores the necessity of building highly effective and resilient bots to compete in the modern data landscape.
Why Build and Use a Scraping Bot?
The decision to build a scraping bot is typically driven by the need for data that is either unavailable through APIs or requires real-time monitoring.
1. Competitive Intelligence and Market Research
Businesses use scraping bots to gain a competitive edge. For example, an e-commerce company can monitor competitor pricing, stock levels, and product descriptions in real-time. This allows for dynamic pricing adjustments, ensuring they remain competitive. This is a core application of web scraping for market research.
2. Content Aggregation and Lead Generation
Media companies and specialized platforms use bots to aggregate content from various sources, creating a centralized, valuable resource for their users. Similarly, sales teams use bots to extract contact information and company details from public directories, fueling their lead generation pipelines.
3. Automation and Efficiency
A scraping bot can perform tasks in minutes that would take a human hundreds of hours. This efficiency is critical for tasks like financial data collection, academic research, and monitoring compliance across thousands of web pages. The ability to automate this process is the primary reason why companies invest in learning how to build a scraping bot. The landmark case of hiQ Labs, Inc. v. LinkedIn Corp. further clarified the legality of scraping publicly available data.
How to Build Your Scraping Bot: Step-by-Step Guide
Learning how to build a scraping bot involves a structured approach, moving from initial planning to deployment and maintenance.
Step 1: Define Scope and Ethics
Before writing any code, clearly define the data points you need and the target websites. Crucially, you must check the website's robots.txt file, which specifies which parts of the site crawlers are allowed to access. Always adhere to the site's terms of service. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to IP bans, legal action, or ethical violations. For a detailed understanding of compliance, consult Google's official guide on robots.txt.
Step 2: Choose the Right Technology Stack
The technology stack is determined by the target website's complexity. For modern sites, a browser automation framework is mandatory.
| Component | Static Sites (Simple) | Dynamic Sites (Complex) |
|---|---|---|
| Language | Python, Node.js | Python, Node.js |
| HTTP Client | requests (Python) |
Handled by the browser automation tool |
| Parser | BeautifulSoup, lxml |
Playwright, Puppeteer (using their built-in DOM access) |
| Framework | None/Custom Script | Scrapy, Scrapy-Playwright |
| Security | Basic User-Agent rotation | Proxies, CAPTCHA Solvers, Fingerprint Management |
For a robust scraping bot tutorial 2026, we recommend Python due to its rich ecosystem of Top Python Web Scraping Libraries 2026. Scrapy, in particular, is a powerful framework for large-scale projects.
Step 3: Implement Security Navigation Techniques
This is the most challenging part of web scraping. Websites actively employ security measures to prevent unauthorized automated data extraction.
A. Request Throttling and IP Rotation
To avoid rate limiting, your bot must introduce random delays between requests. More importantly, you must use a reliable proxy network to rotate your IP address. This makes it appear as if requests are coming from many different users. Learn effective strategies to How to Avoid IP Bans when Using Captcha Solver in 2026.
B. Handling Dynamic Content and Fingerprinting
Use a headless browser like Playwright to ensure JavaScript is executed, rendering the page exactly as a human user would see it. Playwright Official Documentation shows it is often preferred over older tools like Selenium because it offers better control over browser fingerprinting, which is a key method security systems use to identify bots.
C. CAPTCHA Resolution
When a CAPTCHA challenge appears, your bot cannot proceed. You must integrate a specialized service to resolve it. These services use AI to solve image and text challenges automatically. Choosing the right CAPTCHA solver is crucial for maintaining the bot's uptime. You can compare The Best 5 Captcha Solvers for Web Scraping in 2026 to find the most reliable option. For instance, you can integrate a Best reCAPTCHA Solver 2026 for Automation & Web Scraping to handle common challenges.
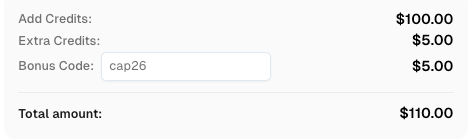
Use code
CAP26when signing up at CapSolver to receive bonus credits!
Step 4: Data Cleaning, Storage, and Scheduling
Once the data is extracted, it must be cleaned (e.g., removing HTML tags, standardizing formats) and stored. For continuous operation, the bot must be scheduled to run periodically using tools like Cron jobs or cloud-native schedulers. This ensures your data remains fresh and relevant for web scraping for market research.
Step 5: Monitoring and Maintenance
Websites change their structure frequently. Your scraping bot will inevitably break. Implement robust logging and monitoring to alert you when the bot fails. Regular maintenance and adapting your selectors to new website layouts are ongoing tasks for any successful scraping bot operator.
Case Study: E-commerce Price Monitoring Bot
A medium-sized electronics retailer needed to monitor the prices of their top 500 products across three major competitor websites every hour.
- Challenge: Competitor sites used aggressive security measures, including Cloudflare's Turnstile and advanced browser fingerprinting.
- Solution: They built a distributed scraping bot using Scrapy-Playwright, deployed on a cloud platform. They integrated a premium proxy service for IP rotation and used a specialized service to resolve Cloudflare challenges.
- Result: The bot achieved a 99% success rate, providing real-time pricing data that allowed the retailer to implement a dynamic pricing strategy. Within six months, this strategy led to a 12% increase in sales volume for the monitored products. This demonstrates the power of a well-engineered scraping bot.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Understanding what is a scraping bot and how to build one is no longer optional; it is a fundamental skill in the data-driven economy. A sophisticated scraping bot is a powerful tool for automated data extraction, offering unparalleled efficiency and depth in market intelligence. Success hinges on robust security navigation techniques, a modern tech stack, and a commitment to ethical scraping practices.
To ensure your bot remains operational against the most advanced security defenses, you need reliable tools. Explore how a professional CAPTCHA solver can integrate seamlessly into your bot's workflow, guaranteeing continuous data flow even when faced with complex challenges.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is building a scraping bot legal?
The legality of web scraping is complex and highly dependent on jurisdiction, the website's terms of service, and the nature of the data. Generally, scraping publicly available data is often permissible, but scraping data behind a login or violating a site's robots.txt file is risky. Always seek legal counsel and prioritize ethical practices.
Q2: What is the difference between a scraping bot and a web crawler?
A web crawler (like Googlebot) is designed to index the entire web or a large part of it, focusing on discovering links and mapping the internet structure. A scraping bot is highly targeted, focusing on extracting specific data points from a limited set of pages or websites. A scraping bot often incorporates crawling functionality, but its primary goal is data extraction, not indexing.
Q3: How can I prevent my scraping bot from getting blocked?
The most effective strategy is to mimic human behavior: use a headless browser, rotate IP addresses with high-quality proxies, introduce random delays between requests, and manage your browser's fingerprint. When challenges like CAPTCHA or Cloudflare appear, integrate a specialized security challenge resolution service to resolve them automatically.
Q4: What is the role of AI in modern scraping bots?
AI is transforming web scraping in two main ways: first, in resolving security challenges (AI-powered CAPTCHA solvers); and second, in data parsing. LLMs can be used to extract structured data from highly unstructured text (e.g., product reviews or news articles), a task that traditional selector-based bots struggle with.
Q5: Can I use a free proxy for my scraping bot?
Free proxies are highly unreliable, slow, and often already blacklisted by major websites. They will significantly increase your block rate and compromise the integrity of your data. For any serious web scraping project, you must invest in a premium residential or ISP proxy service.
Compliance Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. CapSolver is committed to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The use of the CapSolver network for illegal, fraudulent, or abusive activities is strictly prohibited and will be investigated. Our captcha-solving solutions enhance user experience while ensuring 100% compliance in helping solve captcha difficulties during public data crawling. We encourage responsible use of our services. For more information, please visit our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
More
Browser Automation for Developers: Mastering Selenium & CAPTCHA in 2026
Master browser automation for developers with this 2026 guide. Learn Selenium WebDriver Java, Actions Interface, and how to solve CAPTCHA using CapSolver.

Adélia Cruz
02-Mar-2026
PicoClaw Automation: A Guide to Integrating CapSolver API
Learn to integrate CapSolver with PicoClaw for automated CAPTCHA solving on ultra-lightweight $10 edge hardware.

Ethan Collins
26-Feb-2026

How to Solve Captcha in Nanobot with CapSolver
Automate CAPTCHA solving with Nanobot and CapSolver. Use Playwright to solve reCAPTCHA and Cloudflare autonomously.

Ethan Collins
26-Feb-2026
How to Extract Structured Data From Popular Websites
Learn how to extract structured data from popular websites. Discover tools, techniques, and best practices for web scraping and data analysis.

Aloísio Vítor
12-Feb-2026

Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is and Why It Matters in 2026
Understand Data as a Service (DaaS) in 2026. Explore its benefits, use cases, and how it transforms businesses with real-time insights and scalability.

Emma Foster
12-Feb-2026

How to Fix Common Web Scraping Errors in 2026
Master fixing diverse web scraper errors like 400, 401, 402, 403, 429, 5xx, and Cloudflare 1001 in 2026. Learn advanced strategies for IP rotation, headers, and adaptive rate limiting with CapSolver.

Lucas Mitchell
05-Feb-2026