How to Extract Structured Data From Popular Websites

Aloísio Vítor
Image Processing Expert
12-Feb-2026
Key Takeaways
- Structured data extraction (web scraping) is crucial for market research, lead generation, data aggregation, and academic studies.
- Methods range from manual copy-pasting to browser extensions, programming libraries (Python), and official APIs.
- Python libraries like Beautiful Soup and Scrapy are powerful tools for programmatic scraping.
- APIs are the preferred method for data access when available due to their reliability and structure.
- Ethical and legal considerations are paramount: always check
robots.txt, Terms of Service, respect server load, and be mindful of data privacy laws. - CAPTCHA solving services like CapSolver can help overcome security measures.
- Tools like Selenium are necessary for scraping JavaScript-heavy websites.
- Responsible scraping involves delays, rate limiting, and respecting website policies.
Introduction
Did you know that over 95% of websites are not explicitly structured for data extraction? This means that while the information is there, accessing it in a usable, organized format requires specific techniques. The internet is a vast ocean of information, but much of it exists as unstructured text and images. For businesses, researchers, and developers, the ability to systematically extract this data – to turn raw web content into actionable insights – is becoming increasingly vital. This process, often referred to as web scraping, allows us to collect information from websites programmatically, transforming the chaotic web into a treasure trove of structured data.
This guide will delve into the world of structured data extraction from popular websites. We'll explore why it's important, the different methods available, the tools you can use, and crucial ethical and legal considerations. Whether you're looking to analyze market trends, gather competitive intelligence, or build a new data-driven application, understanding how to extract structured data is a powerful skill.
Why Extract Structured Data?
Before we dive into the 'how,' let's understand the 'why.' Structured data is information organized in a predefined format, making it easy for computers to read and process. Extracting this data from websites offers a multitude of benefits:
1. Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Businesses can gain a significant edge by monitoring competitors' pricing, product offerings, customer reviews, and marketing strategies. By scraping this data, companies can:
- Track competitor pricing in real-time: This allows for dynamic pricing adjustments and staying competitive. According to a report by Statista, 65% of companies engage in competitive pricing analysis as a key strategy.
- Identify market trends: Analyzing product descriptions, customer sentiment, and trending topics can reveal emerging market needs and opportunities.
- Understand customer sentiment: Scraping reviews and social media mentions provides invaluable feedback on products and services.
2. Lead Generation
Sales and marketing teams can use web scraping to identify potential leads. For example, scraping business directories, company websites, or professional networking sites can yield contact information, job titles, and company details, all crucial for targeted outreach.
3. Data Aggregation and Comparison
For platforms that aggregate information from various sources – like travel booking sites, real estate portals, or job boards – web scraping is the backbone. It allows them to collect listings, prices, and details from numerous providers and present them in a unified, searchable format.
4. Academic Research
Researchers across various disciplines, from sociology and economics to computer science, use web scraping to collect data for their studies. This could involve analyzing online discourse, tracking the spread of information, or studying user behavior on digital platforms.
5. Training Machine Learning Models
Machine learning algorithms require vast amounts of data to learn and improve. Web scraping is a primary method for acquiring the datasets needed to train models for tasks like natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics.
Methods of Extracting Structured Data
There are several approaches to extracting structured data, ranging from simple manual methods to sophisticated automated techniques.
1. Manual Data Extraction
This is the most basic method, involving manually copying and pasting information from a website into a spreadsheet or database. While simple, it's incredibly time-consuming, prone to human error, and impractical for large-scale data collection. It's only feasible for very small, one-off tasks.
2. Using Browser Extensions and Tools
Several user-friendly browser extensions and no-code/low-code tools are designed to simplify web scraping for non-programmers. These tools often allow you to visually select the data you want to extract and then export it in formats like CSV or Excel.
- Examples: Octoparse, ParseHub, Web Scraper (Chrome Extension), Data Miner.
- Pros: Easy to use, no coding required, quick for simple tasks.
- Cons: Limited flexibility for complex websites, may struggle with dynamic content or anti-scraping measures, can be expensive for advanced features.
3. Programming Libraries and Frameworks
For more complex scraping needs, flexibility, and scalability, programming is the way to go. Python is a popular choice due to its extensive libraries for web scraping.
-
Key Python Libraries:
- Beautiful Soup: A library for pulling data out of HTML and XML files. It creates a parse tree for parsed pages that can be used to extract data easily.
- Scrapy: A powerful and fast-first open-source web crawling and scraping framework. It's designed to handle large amounts of data and complex scraping tasks.
- Requests: Used to send HTTP requests to get the HTML content of a webpage. It's often used in conjunction with Beautiful Soup.
- Selenium: A tool for automating web browsers. It's particularly useful for scraping websites that rely heavily on JavaScript to load content dynamically.
-
Pros: Highly flexible, scalable, can handle complex websites and anti-scraping measures, cost-effective (open-source libraries).
-
Cons: Requires programming knowledge, steeper learning curve.
4. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
Many websites offer official APIs that allow developers to access their data in a structured format. This is the ideal method when available, as it's sanctioned by the website owner, usually more reliable, and less likely to break due to website changes.
- How it works: You make a request to the API endpoint with appropriate credentials (if required), and the API returns data in a structured format, typically JSON or XML.
- Examples: Twitter API, Google Maps API, Reddit API.
- Pros: Legitimate, reliable, structured data, often faster and more efficient than scraping.
- Cons: Not all websites offer public APIs, APIs may have usage limits or require payment, data might be less comprehensive than what's visible on the website.
5. CAPTCHA Solving Services
Many popular websites implement CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) to prevent automated access. To overcome this, specialized services exist that can solve CAPTCHAs programmatically. These services often use a combination of human solvers and advanced algorithms. For instance, CapSolver is a service that offers efficient CAPTCHA solving solutions, allowing automated scripts to bypass these security measures and continue data extraction.
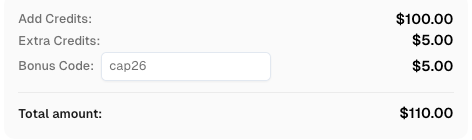
Use code
CAP26when signing up at CapSolver to receive bonus credits!
Steps to Extract Structured Data from Popular Websites
Let's outline a general process for web scraping, focusing on using programming methods (like Python) as they offer the most power and flexibility.
Step 1: Define Your Goal and Target Websites
- What data do you need? Be specific. (e.g., product names, prices, descriptions, reviews, contact info).
- Which websites contain this data? Identify the most relevant and reliable sources.
- Is there an API available? Always check for an official API first. If yes, use it.
Step 2: Analyze the Website Structure
- Inspect the HTML: Use your browser's developer tools (usually by right-clicking on an element and selecting 'Inspect' or 'Inspect Element') to view the HTML source code. Identify the HTML tags, classes, and IDs that contain the data you need.
- Understand website navigation: How do you get to the pages with the data? Do you need to click buttons, scroll, or submit forms?
- Check for JavaScript rendering: If content loads dynamically after the initial page load, you might need tools like Selenium or consider the website's underlying AJAX calls.
Step 3: Choose Your Tools
Based on your analysis and technical skills, select the appropriate tools. For Python, a common stack is Requests + Beautiful Soup for static sites, or Selenium for dynamic sites.
Step 4: Write Your Scraper Script
- Fetch the HTML: Use
Requeststo download the HTML content of the target page. - Parse the HTML: Use
Beautiful Soupto parse the HTML content, making it searchable. - Locate the data: Use CSS selectors or XPath expressions to pinpoint the specific elements containing your desired data (e.g.,
soup.find_all('div', class_='product-title')). - Extract the data: Pull out the text or attributes from the located elements.
- Handle pagination and navigation: If the data spans multiple pages, implement logic to navigate through them (e.g., finding the 'next page' link and repeating the process).
- Implement error handling: Websites can change, or network issues can occur. Your script should gracefully handle errors.
- Consider CAPTCHAs: If you encounter CAPTCHAs, you may need to integrate a CAPTCHA solving service like CapSolver to proceed.
Step 5: Store the Data
Once extracted, the data needs to be stored. Common formats include:
- CSV (Comma Separated Values): Simple, widely compatible format, great for spreadsheets.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): Hierarchical format, excellent for web applications and APIs.
- Databases: For large-scale or complex data, storing in SQL (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL) or NoSQL (e.g., MongoDB) databases is recommended.
Step 6: Respect Website Policies and Be Ethical
This is arguably the most crucial step. We'll cover this in detail next.
Ethical and Legal Considerations in Web Scraping
Web scraping exists in a legal and ethical gray area. While collecting publicly available data is generally permissible, there are important boundaries to respect.
1. Check the robots.txt File
Most websites have a robots.txt file (e.g., www.example.com/robots.txt) that outlines which parts of the site web crawlers (bots) are allowed or disallowed to access. Always respect these directives. Violating robots.txt can lead to your IP address being blocked and is considered unethical.
2. Review the Website's Terms of Service (ToS)
Many websites explicitly prohibit scraping in their Terms of Service. Violating the ToS can have legal consequences, including potential lawsuits. While enforcement varies, it's best practice to adhere to these terms.
3. Avoid Overloading the Server
Aggressive scraping can overwhelm a website's server, slowing it down or even causing it to crash for legitimate users. This is detrimental to the website owner and other users.
- Best Practices:
- Introduce delays: Add pauses (
time.sleep()in Python) between your requests. - Limit request rate: Don't send too many requests per second.
- Scrape during off-peak hours: If possible, target times when the website experiences less traffic.
- Use appropriate User-Agent strings: Identify your scraper as a bot, but avoid overly aggressive or misleading user agents.
- Introduce delays: Add pauses (
4. Data Privacy (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
Be extremely cautious when scraping personal data. Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) impose strict rules on collecting, storing, and processing personal information. Scraping and using personal data without consent can lead to severe legal penalties.
5. Intellectual Property Rights
Content on websites is often protected by copyright. While scraping might be technically possible, republishing or commercializing scraped copyrighted content without permission can lead to infringement claims.
6. Legal Precedents
Recent court cases have further clarified the legal landscape. For example, the LinkedIn v. hiQ Labs case highlighted that scraping publicly available data from a platform that is not behind a login might be permissible, but scraping data behind a login without authorization is generally not.
Advanced Techniques and Tools
As you become more proficient, you might explore:
1. Headless Browsers
Tools like Selenium or Puppeteer (for Node.js) can control browsers in the background without a visible UI. This is essential for scraping JavaScript-heavy websites where content is loaded dynamically.
2. Proxy Servers
To avoid IP bans, especially when scraping at scale, you can route your requests through proxy servers. This makes your requests appear to come from different IP addresses. Services offer rotating proxy pools for this purpose.
3. CAPTCHA Solving Services
As mentioned earlier, for websites that employ CAPTCHAs, services like CapSolver are indispensable for maintaining scraping operations. These services automate the process of solving CAPTCHAs, ensuring your scripts aren't halted by these security measures.
4. Distributed Scraping
For very large-scale operations, distributing the scraping workload across multiple machines or servers can significantly speed up data collection.
Conclusion
Extracting structured data from popular websites is a powerful capability that unlocks a wealth of information for analysis, decision-making, and innovation. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or a business professional, understanding the principles and tools of web scraping can provide a significant advantage. However, it's crucial to approach this practice with a strong sense of ethics and a clear understanding of the legal boundaries. By respecting website policies, being mindful of server load, and prioritizing data privacy, you can harness the power of the web responsibly and effectively. Remember to always check for official APIs first, as they offer the most reliable and sanctioned method for data access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is web scraping legal?
A1: The legality of web scraping is complex and depends on several factors, including the website's terms of service, the robots.txt file, and the nature of the data being scraped (especially if it's personal data). Scraping publicly available data without violating terms or robots.txt is often considered permissible, but scraping data behind logins or personal information without consent can have legal repercussions. Always consult legal counsel if you have specific concerns.
Q2: How can I prevent my IP address from being blocked?
A2: To avoid IP blocking, you can use techniques like rotating proxy servers, introducing delays between requests, limiting your scraping rate, and using ethical User-Agent strings. Some advanced users also employ CAPTCHA solving services when necessary.
Q3: What is the difference between web scraping and an API?
A3: An API (Application Programming Interface) is a structured way for applications to communicate and exchange data, usually provided by the website owner. Web scraping, on the other hand, is the process of extracting data directly from a website's HTML, often when no API is available. APIs are generally preferred as they are sanctioned, more reliable, and provide data in a pre-structured format.
Q4: Can I scrape any website?
A4: While you can technically attempt to scrape almost any website, whether you should or can legally and ethically is another matter. You must respect the website's robots.txt file and Terms of Service. Websites with strong anti-scraping measures or those containing sensitive personal data require particular caution.
Q5: What are the best tools for beginners to start web scraping?
A5: For beginners with no coding experience, browser extensions and no-code tools like Octoparse or ParseHub are excellent starting points. If you're comfortable with some coding, Python libraries like Beautiful Soup and Requests offer a gentler introduction to programmatic scraping compared to frameworks like Scrapy.
Q6: How do I handle websites that use JavaScript to load content?
A6: Websites that heavily rely on JavaScript to load content dynamically often require tools that can render JavaScript. Selenium is a popular choice for this, as it automates a real web browser. Other methods include analyzing the website's network requests (AJAX calls) to directly fetch the data, which can be more efficient than using a full browser automation tool.
Compliance Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. CapSolver is committed to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The use of the CapSolver network for illegal, fraudulent, or abusive activities is strictly prohibited and will be investigated. Our captcha-solving solutions enhance user experience while ensuring 100% compliance in helping solve captcha difficulties during public data crawling. We encourage responsible use of our services. For more information, please visit our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
More
How to Extract Structured Data From Popular Websites
Learn how to extract structured data from popular websites. Discover tools, techniques, and best practices for web scraping and data analysis.

Aloísio Vítor
12-Feb-2026

Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is and Why It Matters in 2026
Understand Data as a Service (DaaS) in 2026. Explore its benefits, use cases, and how it transforms businesses with real-time insights and scalability.

Emma Foster
12-Feb-2026

How to Fix Common Web Scraping Errors in 2026
Master fixing diverse web scraper errors like 400, 401, 402, 403, 429, 5xx, and Cloudflare 1001 in 2026. Learn advanced strategies for IP rotation, headers, and adaptive rate limiting with CapSolver.

Lucas Mitchell
05-Feb-2026

How to Solve Captcha with Nanobrowser and CapSolver Integration
Solve reCAPTCHA and Cloudflare Turnstile automatically by integrating Nanobrowser with CapSolver for seamless AI automation.

Ethan Collins
04-Feb-2026

How to Solve Captcha in RoxyBrowser with CapSolver Integration
Integrate CapSolver with RoxyBrowser to automate browser tasks and bypass reCAPTCHA, Turnstile, and other CAPTCHAs.

Lucas Mitchell
04-Feb-2026

How to Solve Captcha in EasySpider with CapSolver Integration
EasySpider is a visual, no-code web scraping and browser automation tool, and when combined with CapSolver, it can reliably solve CAPTCHAs like reCAPTCHA v2 and Cloudflare Turnstile, enabling seamless automated data extraction across websites.

Lucas Mitchell
04-Feb-2026