Web Scraping with Selenium and Python | Solving Captcha When Web Scraping

Ethan Collins
Pattern Recognition Specialist
19-Jun-2024
Imagine that you can easily get all the data you need from the Internet without having to manually browse the web or copy and paste. That's the beauty of web scraping. Whether you are a data analyst, market researcher, or developer, web scraping opens up a whole new world of automated data collection.
In this data-driven era, information is power. However, manually extracting information from hundreds or even thousands of web pages is not only time-consuming, but also error-prone. Fortunately, Web scraping provides an efficient and accurate solution that allows you to automate the process of extracting the data you need from the Internet, thus greatly improving efficiency and data quality.
Table of Content
What is Web Scraping?
Web scraping is a technique for automatically extracting information from web pages by writing programmes. This technology has a wide range of applications in many fields, including data analysis, market research, competitive intelligence, content aggregation, and more. With Web scraping, you can collect and consolidate data from a large number of web pages in a short period of time, rather than relying on manual operations.
The process of Web scraping usually includes the following steps:
- Send HTTP request: Programmatically send a request to the target website to get the HTML source code of the web page. Commonly used tools such as Python's requests library can do this easily.
- Parsing HTML content: After obtaining the HTML source code, it needs to be parsed in order to extract the required data. HTML parsing libraries such as BeautifulSoup or lxml can be used to process the HTML structure.
- Extracting data: Based on the parsed HTML structure, locate and extract specific content, such as article title, price information, image links, etc. Common methods include using XPath or CSS selectors.
- Store data: Save the extracted data to a suitable storage medium, such as a database, CSV file or JSON file, for subsequent analysis and processing.
And which, by using tools such as Selenium, can simulate the operation of the user's browser, bypassing some of the anti-crawler mechanisms, so as to complete the Web scraping task more efficiently.
Redeem Your CapSolver Bonus Code
Boost your automation budget instantly!
Use bonus code CAPN when topping up your CapSolver account to get an extra 5% bonus on every recharge — with no limits.
Redeem it now in your CapSolver Dashboard
.
Getting Started with Selenium
Let's take ScrapingClub as an example and use selenium to complete exercise one.
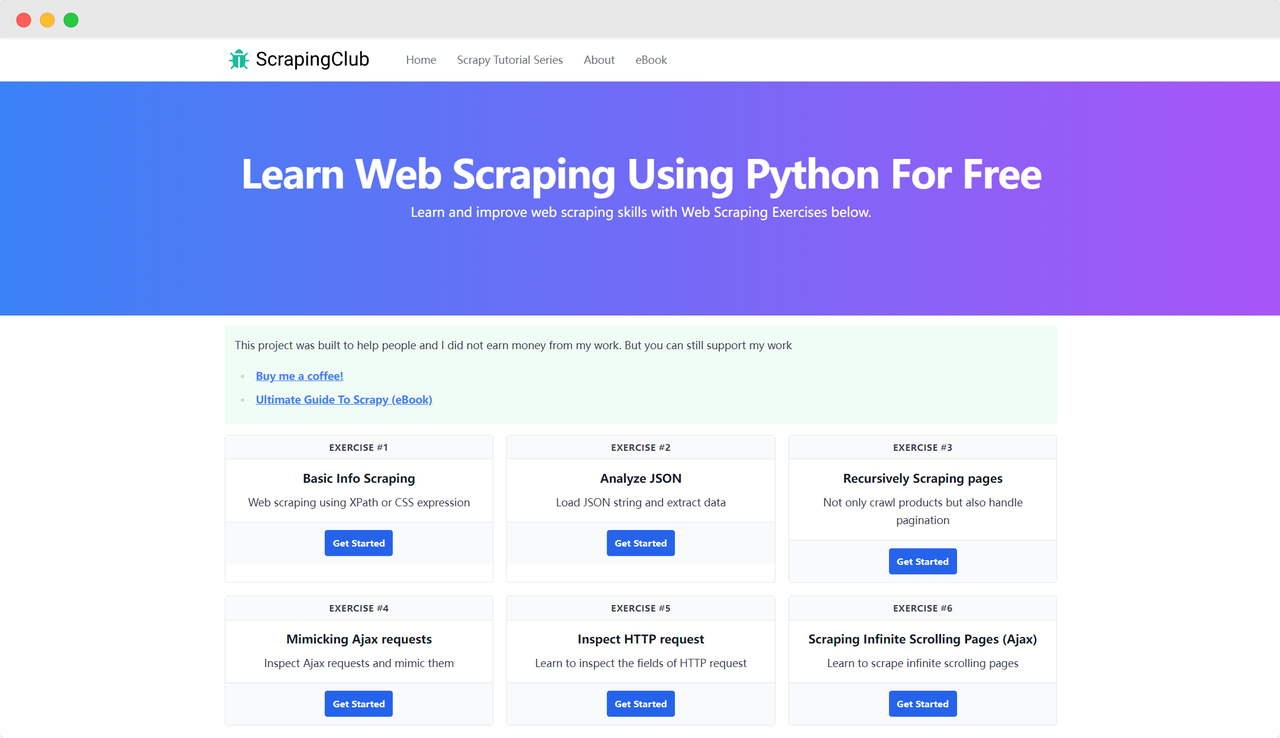
Preparation
First, you need to ensure that Python is installed on your local machine. You can check the Python version by entering the following command in your terminal:
bash
python --versionMake sure the Python version is greater than 3. If it is not installed or the version is too low, please download the latest version from the Python official website. Next, you need to install the selenium library using the following command:
bash
pip install seleniumImport Libraries
python
from selenium import webdriverAccessing a Page
Using Selenium to drive Google Chrome to access a page is not complicated. After initializing the Chrome Options object, you can use the get() method to access the target page:
python
import time
from selenium import webdriver
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
driver.get('https://scrapingclub.com/')
time.sleep(5)
driver.quit()Startup Parameters
Chrome Options can add many startup parameters that help improve the efficiency of data retrieval. You can view the complete list of parameters on the official website: List of Chromium Command Line Switches. Some commonly used parameters are listed in the table below:
| Parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|
| --user-agent="" | Set the User-Agent in the request header |
| --window-size=xxx,xxx | Set the browser resolution |
| --start-maximized | Run with maximized resolution |
| --headless | Run in headless mode |
| --incognito | Run in incognito mode |
| --disable-gpu | Disable GPU hardware acceleration |
Example: Running in Headless Mode
python
import time
from selenium import webdriver
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
chrome_options.add_argument('--headless')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
driver.get('https://scrapingclub.com/')
time.sleep(5)
driver.quit()Locating Page Elements
A necessary step in scraping data is to find the corresponding HTML elements in the DOM. Selenium provides two main methods to locate elements on the page:
find_element: Finds a single element that meets the criteria.find_elements: Finds all elements that meet the criteria.
Both methods support eight different ways to locate HTML elements:
| Method | Meaning | HTML Example | Selenium Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| By.ID | Locate by element ID | <form id="loginForm">...</form> |
driver.find_element(By.ID, 'loginForm') |
| By.NAME | Locate by element name | <input name="username" type="text" /> |
driver.find_element(By.NAME, 'username') |
| By.XPATH | Locate by XPath | <p><code>My code</code></p> |
driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//p/code") |
| By.LINK_TEXT | Locate hyperlink by text | <a href="continue.html">Continue</a> |
driver.find_element(By.LINK_TEXT, 'Continue') |
| By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT | Locate hyperlink by partial text | <a href="continue.html">Continue</a> |
driver.find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT, 'Conti') |
| By.TAG_NAME | Locate by tag name | <h1>Welcome</h1> |
driver.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, 'h1') |
| By.CLASS_NAME | Locate by class name | <p class="content">Welcome</p> |
driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'content') |
| By.CSS_SELECTOR | Locate by CSS selector | <p class="content">Welcome</p> |
driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, 'p.content') |
Let's return to the ScrapingClub page and write the following code to find the "Get Started" button element for exercise one:
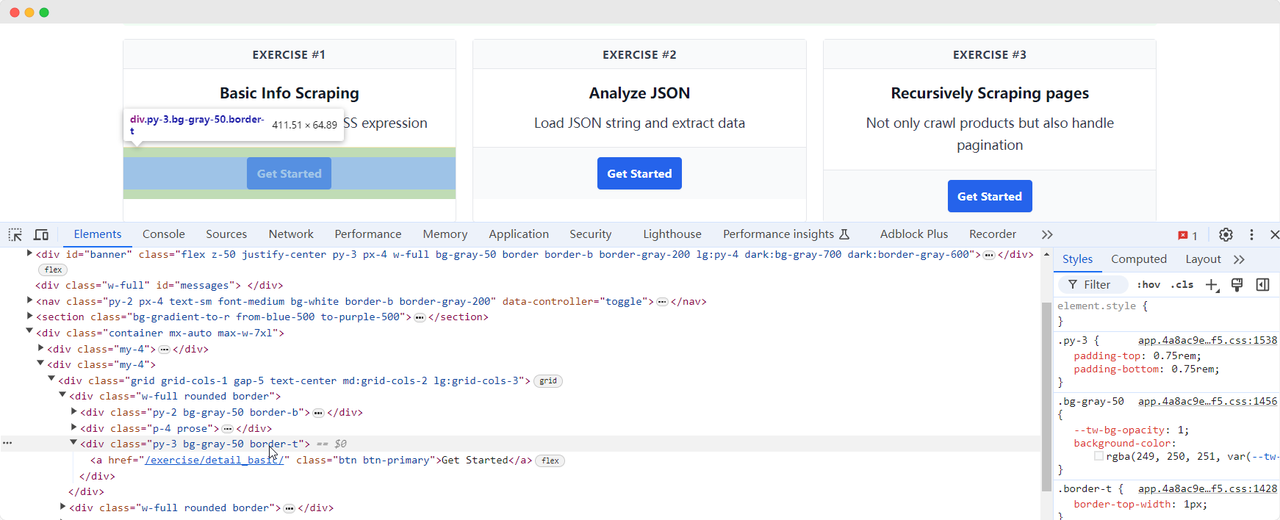
python
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
driver.get('https://scrapingclub.com/')
get_started_button = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//div[@class='w-full rounded border'][1]/div[3]")
time.sleep(5)
driver.quit()Element Interaction
Once we have found the "Get Started" button element, we need to click the button to enter the next page. This involves element interaction. Selenium provides several methods to simulate actions:
click(): Click the element;clear(): Clear the content of the element;send_keys(*value: str): Simulate keyboard input;submit(): Submit a form;screenshot(filename): Save a screenshot of the page.
For more interactions, refer to the official documentation: WebDriver API. Let's continue to improve the ScrapingClub exercise code by adding click interaction:
python
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
driver.get('https://scrapingclub.com/')
get_started_button = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//div[@class='w-full rounded border'][1]/div[3]")
get_started_button.click()
time.sleep(5)
driver.quit()Data Extraction
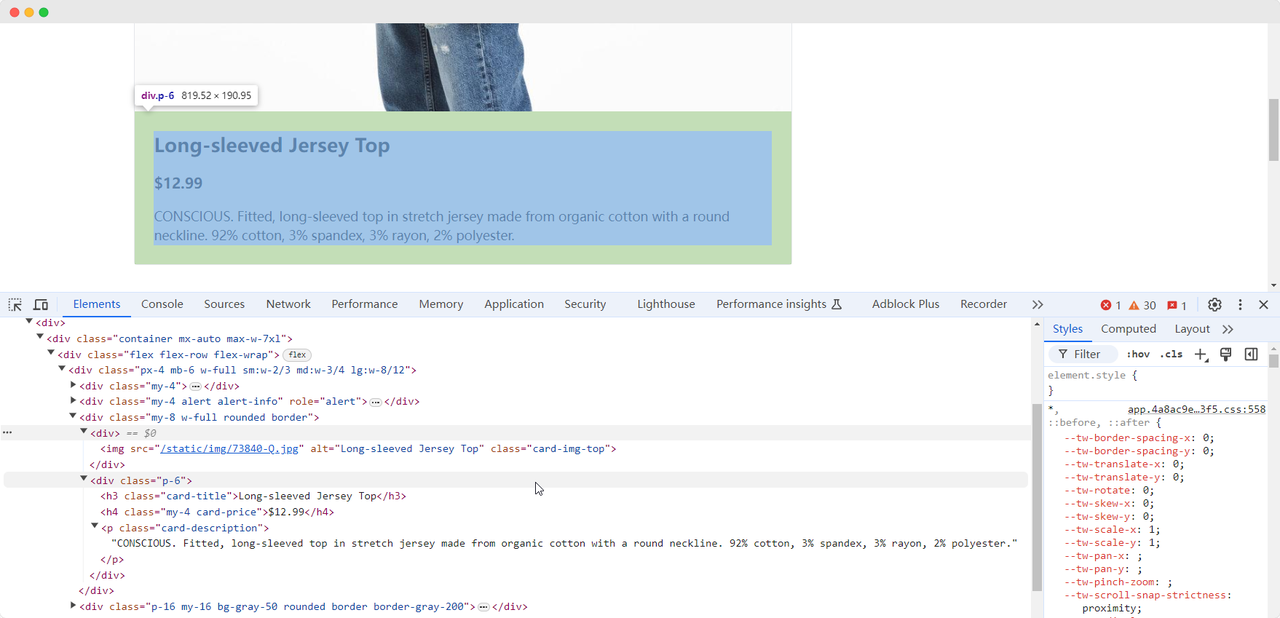
When we arrive at the first exercise page, we need to collect the product's image, name, price, and description information. We can use different methods to find these elements and extract them:
python
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
driver.get('https://scrapingclub.com/')
get_started_button = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//div[@class='w-full rounded border'][1]/div[3]")
get_started_button.click()
product_name = driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'card-title').text
product_image = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.card-img-top').get_attribute('src')
product_price = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//h4').text
product_description = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.card-description').text
print(f'Product name: {product_name}')
print(f'Product image: {product_image}')
print(f'Product price: {product_price}')
print(f'Product description: {product_description}')
driver.quit()The code will output the following content:
Product name: Long-sleeved Jersey Top
Product image: https://scrapingclub.com/static/img/73840-Q.jpg
Product price: $12.99
Product description: CONSCIOUS. Fitted, long-sleeved top in stretch jersey made from organic cotton with a round neckline. 92% cotton, 3% spandex, 3% rayon, 2% polyester.Waiting for Elements to Load
Sometimes, due to network issues or other reasons, elements may not have loaded yet when Selenium finishes running, which can cause some data collection to fail. To solve this problem, we can set it to wait until a certain element is fully loaded before proceeding with data extraction. Here is an example code:
python
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
driver.get('https://scrapingclub.com/')
get_started_button = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//div[@class='w-full rounded border'][1]/div[3]")
get_started_button.click()
# waiting for the product image elements to load completely
wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10)
wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.card-img-top')))
product_name = driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'card-title').text
product_image = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.card-img-top').get_attribute('src')
product_price = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//h4').text
product_description = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.card-description').text
print(f'Product name: {product_name}')
print(f'Product image: {product_image}')
print(f'Product price: {product_price}')
print(f'Product description: {product_description}')
driver.quit()Get Around Anti-Scraping Protections
The ScrapingClub exercise is easy to complete. However, in actual data collection scenarios, obtaining data is not so easy because some websites employ anti-scraping techniques that may detect your script as a bot and block the collection. The most common situation is captcha challenges
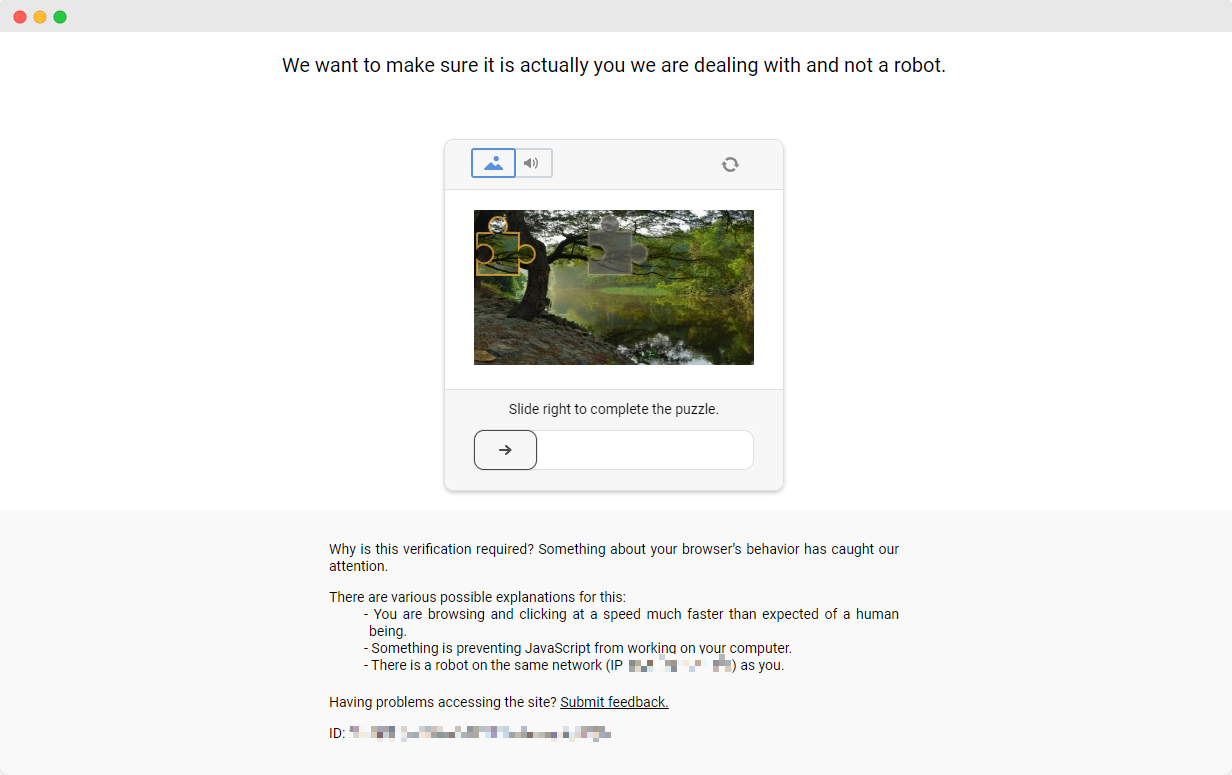
Solving these captcha challenges requires extensive experience in machine learning, reverse engineering, and browser fingerprint countermeasures, which can take a lot of time. Fortunately, now you don't have to do all this work yourself. CapSolver provides a complete solution to help you easily bypass all challenges. CapSolver offers browser extensions that can automatically solve captcha challenges while using Selenium to collect data. Additionally, they provide API methods to solve captchas and obtain tokens, all of which can be completed in just a few seconds. Refer to the CapSolver Documentation for more information.
Conclusion
From extracting product details to navigating through complex anti-scraping measures, web scraping with Selenium opens doors to a vast realm of automated data collection. As we navigate the web's ever-evolving landscape, tools like CapSolver pave the way for smoother data extraction, making once-formidable challenges a thing of the past. So, whether you're a data enthusiast or a seasoned developer, harnessing these technologies not only enhances efficiency but also unlocks a world where data-driven insights are just a scrape away
FAQ
1. What is web scraping used for?
Web scraping is used to automatically extract information from web pages. It allows developers, analysts, and businesses to collect product data, prices, articles, images, reviews, and other online information in bulk without manual copying, greatly improving efficiency and data accuracy.
2. Why use Selenium for web scraping instead of requests or BeautifulSoup?
Requests and BeautifulSoup work well for static web pages, but many modern websites use JavaScript to load content. Selenium simulates a real browser, allowing you to scrape dynamic pages, click buttons, scroll, interact with elements, and bypass simple anti-scraping measures—making it ideal for complex scenarios.
3. Can Selenium scrape websites that require login or user actions?
Yes. Selenium can perform interactions like clicking buttons, typing text, navigating pages, and managing cookies or sessions, making it suitable for scraping pages behind login forms or user workflows.
4. How do I deal with CAPTCHAs when scraping data?
CAPTCHAs are a common anti-bot mechanism that can stop Selenium scripts. Instead of solving them manually, you can integrate solutions such as CapSolver, which provides automatic CAPTCHA solving via API or browser extension to keep the scraping process uninterrupted.
Compliance Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. CapSolver is committed to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The use of the CapSolver network for illegal, fraudulent, or abusive activities is strictly prohibited and will be investigated. Our captcha-solving solutions enhance user experience while ensuring 100% compliance in helping solve captcha difficulties during public data crawling. We encourage responsible use of our services. For more information, please visit our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
More
Browser Automation for Developers: Mastering Selenium & CAPTCHA in 2026
Master browser automation for developers with this 2026 guide. Learn Selenium WebDriver Java, Actions Interface, and how to solve CAPTCHA using CapSolver.

Adélia Cruz
02-Mar-2026
PicoClaw Automation: A Guide to Integrating CapSolver API
Learn to integrate CapSolver with PicoClaw for automated CAPTCHA solving on ultra-lightweight $10 edge hardware.

Ethan Collins
26-Feb-2026

How to Solve Captcha in Nanobot with CapSolver
Automate CAPTCHA solving with Nanobot and CapSolver. Use Playwright to solve reCAPTCHA and Cloudflare autonomously.

Ethan Collins
26-Feb-2026
How to Extract Structured Data From Popular Websites
Learn how to extract structured data from popular websites. Discover tools, techniques, and best practices for web scraping and data analysis.

Aloísio Vítor
12-Feb-2026

Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is and Why It Matters in 2026
Understand Data as a Service (DaaS) in 2026. Explore its benefits, use cases, and how it transforms businesses with real-time insights and scalability.

Emma Foster
12-Feb-2026

How to Fix Common Web Scraping Errors in 2026
Master fixing diverse web scraper errors like 400, 401, 402, 403, 429, 5xx, and Cloudflare 1001 in 2026. Learn advanced strategies for IP rotation, headers, and adaptive rate limiting with CapSolver.

Lucas Mitchell
05-Feb-2026

