CapSolver AI-LLM Architecture in Practice: Building a Decision Pipeline for Adaptive CAPTCHA Recognition Systems

Ethan Collins
Pattern Recognition Specialist
09-Feb-2026

CAPTCHAs have grown increasingly varied and complex — from simple text challenges to interactive puzzles and dynamic risk‑based logic — and today’s automation workflows require more than basic image recognition. Traditional OCR and standalone CNN models struggle to keep up with evolving formats and mixed visual‑semantic tasks.
In our previous article, “AI‑LLM: The Future Solution for Risk Control Image Recognition and CAPTCHA Solving,” we explored why large language models are becoming a key component in modern CAPTCHA systems. This article builds on that by examining the practical architecture behind CapSolver’s AI‑LLM decision pipeline: how different CAPTCHA types are routed to the right solving strategy and how the system adapts as new formats emerge.
The core challenge is not just recognizing pixels but understanding the intent behind a CAPTCHA and adapting in real time. The CapSolver AI‑LLM Architecture blends computer vision with high‑level reasoning to make strategic decisions rather than just pattern matching.
Here’s an overview of that architecture:
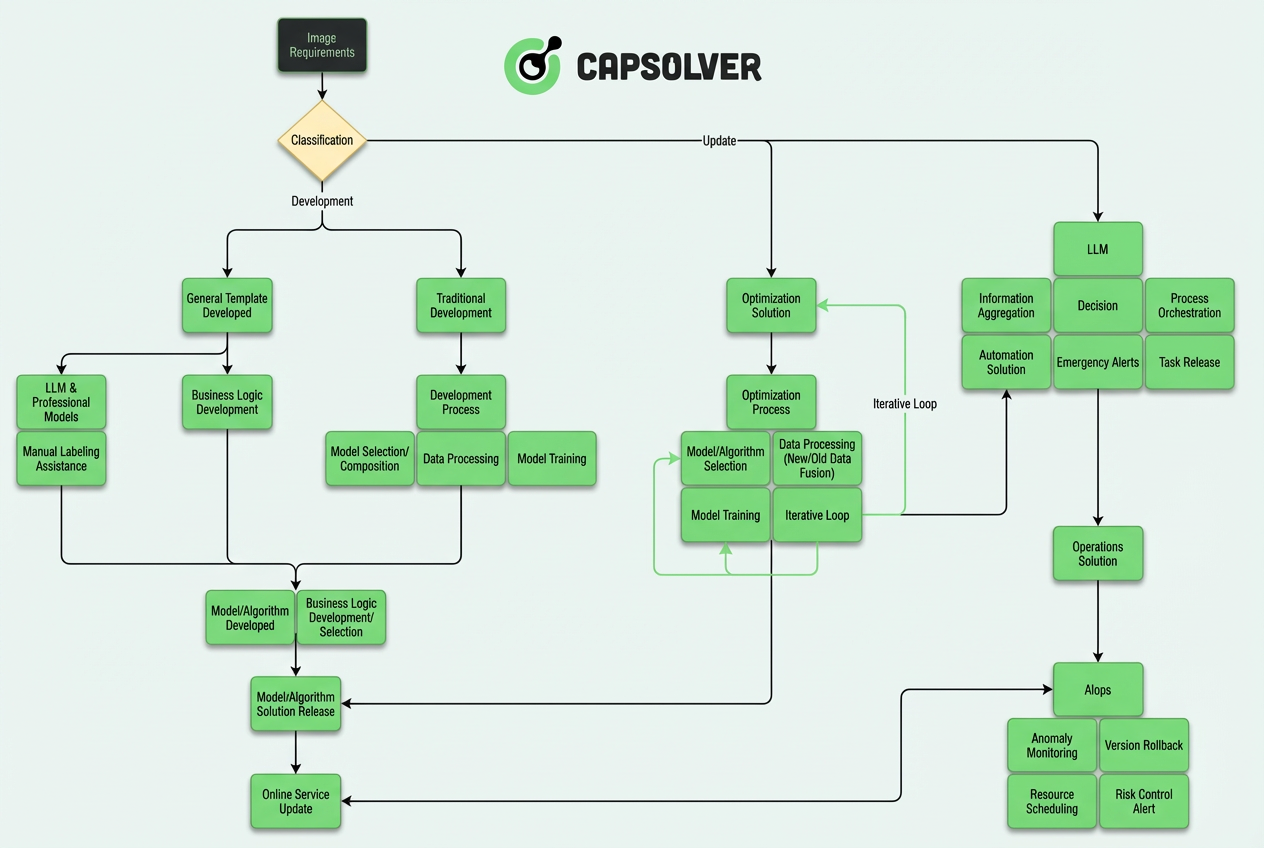
This article dives into the engineering behind our three‑layer autonomous system, bridging raw visual input and semantic reasoning.
According to industry research, by 2026 more than 80% of enterprises will have deployed generative AI‑enabled applications in production environments — highlighting the rapid shift toward automated, AI‑driven workflows and multimodal pipelines.
Core Architecture: Three-Layer Autonomous System
Based on engineering practice, modern CAPTCHA recognition systems have evolved from a "model + rules" monolithic architecture into a complex system of layered autonomy. The entire architecture can be divided into three core layers:
| Layer | Core Module | Functional Positioning | Tech Stack Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application Decision Layer | LLM Brain | Semantic understanding, task orchestration, anomaly analysis | GPT-4/Vision, Claude 3, Qwen3, Self-developed LangChain Agents |
| Algorithm Execution Layer | CV Engine | Object detection, trajectory simulation, image recognition | YOLO, ViT, blip, clip, dino |
| O&M Assurance Layer | AIops | Monitoring, rollback, resource scheduling, risk control | Prometheus, Kubernetes, Custom RL strategies |
The core idea of this layered design is: LLM is responsible for "thinking", CV models are responsible for "execution", and AIops is responsible for "assurance".
Why is LLM intervention needed?
Traditional CAPTCHA recognition faces three fatal bottlenecks:
- Semantic Gap: Inability to understand instructional texts like "Please click all images containing xx" or "Touch the item usually used with the displayed item," while the variety of such questions is increasing.
- Adaptive Lag: When target websites update verification logic, manual re-labeling and training are required (cycles lasting several days).
- Rigid Anomaly Handling: Facing new defense modes (such as adversarial samples), similar types frequently switch versions, and some even autonomously increase the probability of types with low pass rates. Older engines lack autonomous analysis capabilities for such risk controls.
Note: LLM does not replace CV models but becomes the "neural center" of the CV system, giving it the ability to understand and evolve.
Working Mechanism of the Decision Pipeline
The entire system follows a closed-loop process of Perception-Decision-Execution-Evolution, which can be subdivided into four key stages:
Stage 1: Intelligent Routing
When a new image request enters the system, it first passes through an LLM-driven classifier for intelligent routing:
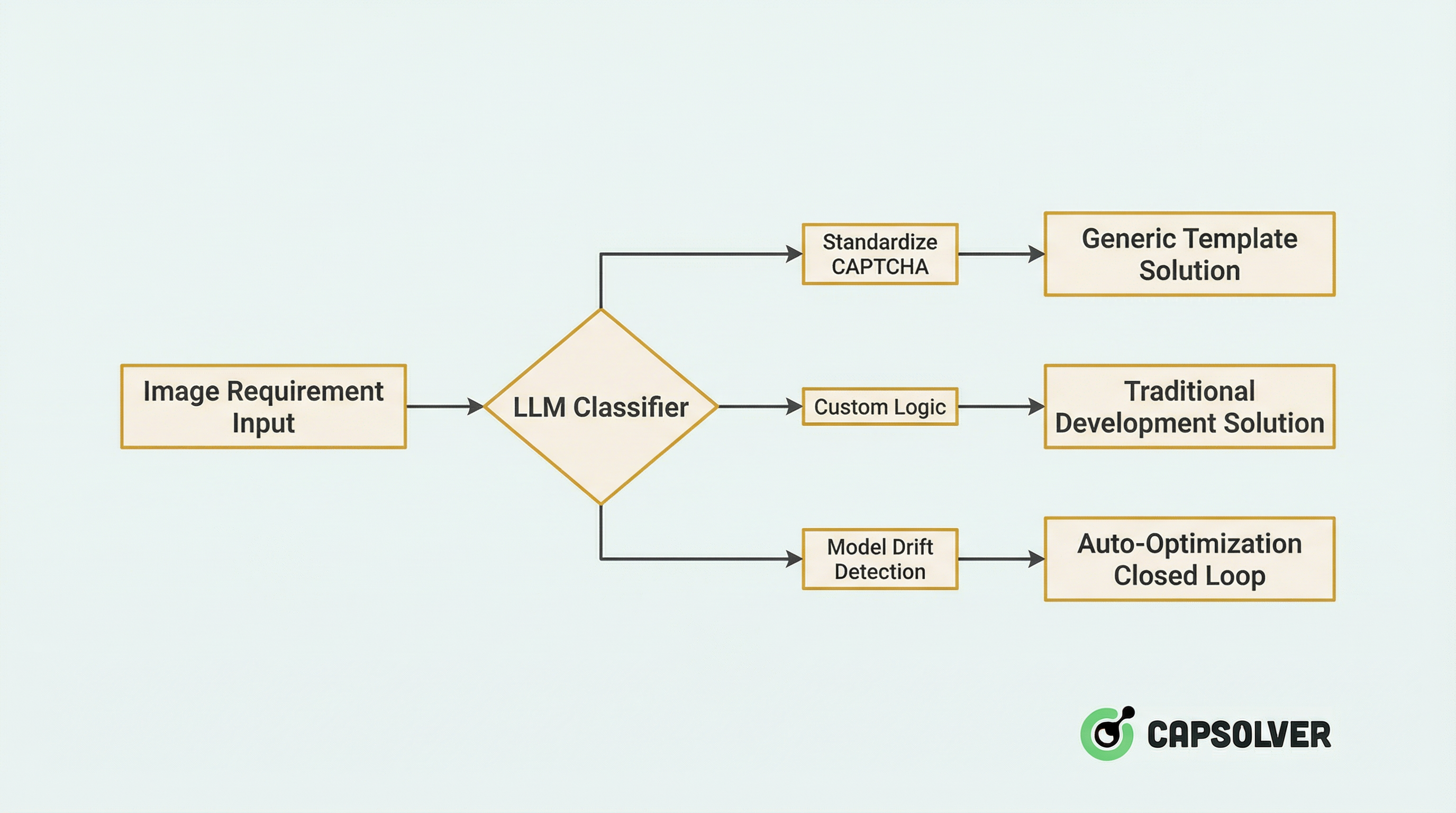
Technical Details:
- Zero-shot Classification: Utilizing the visual understanding capabilities of LLMs to identify CAPTCHA types (slider, click-to-select, rotation, ReCaptcha, etc.) without training.
- Confidence Assessment: When LLM confidence is below 0.8, it automatically triggers a manual review process and incorporates the sample into the incremental training set.
Practical Data: After the platform integrated this routing system, resource allocation efficiency increased by 47%, and the misclassification rate dropped from 12% to 2.1%.
Stage 2: Dual-Track Development
Based on classification results, the system enters two different technical tracks:
Track A: Low-Code Track (Fast Response via General Templates)
Applicable to standardized CAPTCHAs like reCAPTCHA:
Universal Template Library
language
├── LLM Pre-Labeling: Automatically generate bounding boxes and semantic labels
├── Pretrained Models: General detectors trained on millions of samples
└── LLM Post-Processing: Semantic correction (e.g., distinguishing 0/O, 1/l, removing duplicates)Key Innovation — Intelligent Labeling Flywheel:
- LLM generates pseudo-labels through few-shot learning.
- High-quality data corrected by manual review flows back into the training pool.
- Labeling costs are reduced by 60%, while data diversity increases 3-fold.
Track B: Pro-Code Track (Deep Customized Development)
Targeting enterprise-level customized CAPTCHAs (e.g., specific slider algorithms, rotation angle logic):
Traditional Development Pipeline
language
├── Model Selection/Composition (Detection + Recognition + Decision)
├── Data Processing: Cleaning → Labeling → Adversarial Sample Generation (LLM-assisted: Accuracy testing and new data filtering)
└── Continuous Training: Supports incremental learning and domain adaptationRole of LLM in Data Generation:
- Image Generation: Using Diffusion models to generate diverse background images and target images.
- Text Generation: LLM generates adversarial text samples (e.g., distorted, blurred fonts, small images of abstractly drawn real-world objects) or instructional text ("Please click all images containing xx").
- Rule Generation and Variation: Combining text and information to simulate image combination rules and risk control verification mechanisms in real-time via GANs.
- Verification Mechanism: Using ViT-related models to verify and filter data, improving the hit rate of positive samples.
Stage 3: Self-Evolution Loop (Framework Core)
This is the most revolutionary part of the architecture. The system achieves autonomous evolution through the pipeline of AIops → LLM Analysis → Automatic Optimization:
Model Release → Online Service → Anomaly Monitoring → LLM Root Cause Analysis → Generation of Optimization Plan → Automatic Retraining → Canary Release
Six Major Decision Modules of LLM:
| Functional Module | Specific Role | Business Value |
|---|---|---|
| Information Summarization | Aggregates error logs, identifies failure patterns (e.g., "recognition rate drops in night scenes") | Transforms massive logs into actionable insights |
| Intelligent Decision | Determines thresholds for triggering model updates (e.g., accuracy drops >5% for 1 hour) or risk control update alerts (accuracy drops >30% instantly) | Avoids overtraining, saves GPU costs |
| Process Orchestration | Automatically orchestrates the CI/CD pipeline from data collection → labeling → training → testing → release | Shortens iteration cycles from days to hours |
| Automated Solutions | Generates data augmentation strategies (e.g., combining rule-generated backgrounds with newly generated or collected targets) | Zero-manual-intervention data preparation |
| Emergency Alerts | Identifies new attack patterns (e.g., mass production of adversarial samples) and triggers risk control updates | Response time < 5 minutes |
| Task Distribution | Automatically assigns difficult samples to labeling teams with LLM-generated labeling guidelines | Increases labeling efficiency by 40% |
Real Case: When an e-commerce client updated its slider CAPTCHA's gap detection algorithm, traditional systems required 3-5 days of manual adaptation. The LLM-based closed-loop system completed anomaly detection, root cause analysis, data generation, and model fine-tuning within 30 minutes, quickly restoring recognition accuracy from an initial 34% to 96.8%.
Stage 4: Multimodal Execution (Business Expansion)
CAPTCHA recognition is no longer a pure image task but a comprehensive decision-making process integrating vision, semantics, and behavior. Expansion to new types no longer has time and cost limitations.
| CAPTCHA Type | Visual Solution | LLM Enhancement Point |
|---|---|---|
| Slider CAPTCHA | Gap detection (YOLO) + Image comparison + Trajectory simulation | LLM analyzes gap texture features to generate human-like sliding trajectories (avoiding constant speed linear motion identified as bots) |
| Click-to-select CAPTCHA | Object detection + Coordinate positioning | LLM understands semantic instructions (e.g., "Touch the item usually used with the displayed item"), making contextual reasoning in ambiguous scenarios |
| Rotation CAPTCHA | Angle regression prediction | LLM assists in judging visual alignment standards and handling partial occlusion scenarios |
| ReCaptcha v3 | Behavioral biometric analysis | LLM synthesizes mouse trajectories, click intervals, and page scrolling patterns for human-bot judgment |
AIops: The Immune System of Autonomous Systems
Without reliable O&M assurance, even the smartest decision pipeline cannot be put into production. The AIops layer ensures system stability through four core capabilities:
1. Anomaly Detection
- Model Drift Monitoring: Real-time comparison of input data distribution vs. training set distribution (KS test), alerting when drift exceeds thresholds.
- Performance Decay Tracking: Monitoring the three-dimensional metrics of success rate, response latency, and GPU utilization.
2. Smart Rollback
When a new model version performs abnormally, the system not only automatically rolls back to a stable version but also generates a fault diagnosis report via LLM analysis, pointing out possible causes (e.g., "overexposure due to high proportion of night images in new samples").
3. Elastic Resource Scheduling
Auto-scaling based on traffic prediction:
- Peak Periods (e.g., Black Friday): Automatically scales up to 50 GPU instances.
- Off-peak Periods: Scales down to 5 instances, migrating cold data to object storage.
- Cost savings reach 65% while ensuring 99.99% availability.
4. Risk Control and Adversarial Defense
- Adversarial Sample Detection: Identifying CAPTCHA images with adversarial perturbations (FGSM, PGD attacks).
- Behavioral Risk Control: Monitoring abnormal request patterns (e.g., high-frequency requests from a single IP), automatically triggering human-machine verification or IP blocking.
Implementation Path: From POC to Production
Implementation recommendations based on this architecture are divided into four phases:
| Phase | Duration | Key Milestones | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Infrastructure | 1-2 Months | Build AIops monitoring baseline, achieve full-link observability | MTTR (Mean Time To Repair) < 15 minutes |
| Phase 2: Integration | 2-3 Months | LLM integrated into error analysis, achieving automated diagnosis reports | Manual analysis workload reduced by 70% |
| Phase 3: Automation | 3-4 Months | Build fully automated training pipeline (AutoML + LLM) | Model iteration cycle < 4 hours |
| Phase 4: Autonomy | 6-12 Months | Achieve LLM-driven autonomous optimization loop | Manual intervention frequency < 1 time/week |
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Challenge 1: Wrong Decisions Caused by LLM Hallucinations
Solutions:
- Adopt RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architecture, anchoring decision bases in a library of real historical cases.
- Set up manual approval nodes: High-risk operations like model rollback or data deletion require manual confirmation.
Challenge 2: Cost Out of Control
The image analysis cost of GPT-4V is 50-100 times that of traditional CV models.
Solutions:
- Layered Processing: Use lightweight CV models (blip, clip, dino, etc.) for simple scenarios, submitting only difficult samples to LLM.
- Token Budget Management: Set maximum tokens per request to avoid cost spikes from abnormal inputs.
Challenge 3: Latency-Sensitive Scenarios
CAPTCHA recognition usually requires < 2 seconds response.
Solutions:
- Asynchronous Analysis: LLM optimization suggestions are generated via asynchronous processes, not blocking the real-time recognition path.
- Edge Deployment: Deploy lightweight LLMs (e.g., Qwen3-8b, Llama-3-8B) on edge nodes, with processing time < 500ms.
Conclusion: Evolution from Tool to Partner
The CapSolver AI-LLM architecture represents a paradigm shift in the CAPTCHA recognition field from static tools to dynamic agents. Its value lies not only in improving recognition accuracy but also in building a self-evolving technical ecosystem:
- Faster Response: General templates achieve minute-level adaptation.
- Deeper Customization: Traditional development supports complex business logic.
- Continuous Evolution: LLM-driven closed loops ensure the system stays up-to-date.
"Future AI systems will not be maintained by humans, but will be digital partners that collaborate with humans and grow autonomously."
With the continuous evolution of multimodal large models (such as GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro), we have reason to believe that CAPTCHA recognition will no longer be a tedious technical confrontation, but an efficient, secure, and trustworthy automated negotiation process between AI systems.
Try it yourself! Use code
CAP26when signing up at CapSolver to receive bonus credits!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Does adding LLM increase recognition latency?
A: Through layered architecture design, the real-time recognition path is still handled by optimized CV models (latency < 200ms). LLM is mainly responsible for offline analysis and strategy optimization. For complex scenarios requiring semantic understanding, lightweight LLMs deployed at the edge (latency < 500ms) or asynchronous processing modes can be used.
Q2: How to handle potential wrong decisions by LLM?
A: Implement a Human-in-the-loop mechanism: High-risk operations (e.g., full model rollback, data source deletion) require manual approval. Meanwhile, establish a sandbox testing environment where all LLM-generated optimization plans must be validated through A/B testing before full deployment.
Q3: Is this architecture suitable for small teams?
A: Yes. Progressive implementation is recommended: Initially, use only cloud-based LLM APIs (e.g., Claude 3 Haiku) for anomaly analysis without building large models; use open-source tools (LangChain, MLflow) to build pipelines. As the business grows, gradually introduce private deployment and AIops automation.
Q4: How does the cost compare to traditional pure CV solutions?
A: Initial investment increases by about 30-40% (mainly for LLM API calls and engineering transformation), but the reduction in manual O&M costs through automation usually offsets the incremental investment within 3-6 months. In the long run, due to improved model iteration efficiency and higher automation rates, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) can be reduced by more than 50%.
Compliance Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. CapSolver is committed to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The use of the CapSolver network for illegal, fraudulent, or abusive activities is strictly prohibited and will be investigated. Our captcha-solving solutions enhance user experience while ensuring 100% compliance in helping solve captcha difficulties during public data crawling. We encourage responsible use of our services. For more information, please visit our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
More

CapSolver AI-LLM Architecture in Practice: Building a Decision Pipeline for Adaptive CAPTCHA Recognition Systems
Explore CapSolver’s AI-LLM architecture for adaptive CAPTCHA solving, combining vision, reasoning, and autonomous decision-making.

Ethan Collins
09-Feb-2026
Agentic AI News: Why Web Automation Keeps Failing on CAPTCHA
Discover why AI agents struggle with web automation and CAPTCHA. Learn how to bridge the gap between AI reasoning and execution with CapSolver's solutions.

Aloísio Vítor
05-Feb-2026
Crawl4AI vs Firecrawl: Full Comparison & 2026 Review
Compare Crawl4AI vs Firecrawl in 2026. Discover features, pricing, and performance of these AI web scraping tools for LLM-ready markdown extraction.

Anh Tuan
03-Feb-2026
Browser Use vs Browserbase: Which Browser Automation Tool Is Better for AI Agents?
Compare Browser Use vs Browserbase for AI agent automation. Discover features, pricing, and how to solve CAPTCHAs with CapSolver for seamless workflows.

Anh Tuan
27-Jan-2026

Top 9 AI Agent Frameworks in 2026
Explore the top 9 AI agent frameworks for 2026, including CrewAI, AutoGen, and LangGraph. Learn how to choose the best framework for multi-agent orchestration and autonomous agent development, and discover essential tools for real-world web interaction.

Emma Foster
26-Jan-2026
Top Data Extraction Tools to Use in 2026 (Full Comparison)
Discover the best data extraction tools for 2026. Compare top web scraping, ETL, and AI-powered platforms to automate your data collection and AI workflows.

Sora Fujimoto
20-Jan-2026