How to Solve Captchas When Web Scraping with Scrapling and CapSolver

Ethan Collins
Pattern Recognition Specialist
04-Dec-2025

Key Takeaways
- Scrapling is a powerful Python web scraping library with built-in anti-bot features and adaptive element tracking
- CapSolver provides automated captcha solving for ReCaptcha v2, v3, and Cloudflare Turnstile with fast resolution times (1-20 seconds)
- Combining Scrapling with CapSolver creates a robust scraping solution that handles most captcha-protected websites
- StealthyFetcher adds browser-level anti-detection when basic HTTP requests aren't enough
- All three captcha types use the same CapSolver workflow: create task → poll for results → inject token
- Production code should include error handling, rate limiting, and respect for website terms of service
Introduction
Web scraping has become an essential tool for data collection, market research, and competitive analysis. However, as scraping techniques have evolved, so have the defenses websites use to protect their data. Among the most common obstacles scrapers face are captchas — those annoying challenges designed to distinguish humans from bots.
If you've ever tried to scrape a website only to be met with a "Please verify you're human" message, you know the frustration. The good news? There's a powerful combination that can help: Scrapling for intelligent web scraping and CapSolver for automated captcha solving.
In this guide, we'll walk through everything you need to know to integrate these tools and successfully scrape captcha-protected websites. Whether you're dealing with Google's ReCaptcha v2, the invisible ReCaptcha v3, or Cloudflare's Turnstile, we've got you covered.
What is Scrapling?
Scrapling is a modern Python web scraping library that describes itself as "the first adaptive scraping library that learns from website changes and evolves with them." It's designed to make data extraction easy while providing powerful anti-bot capabilities.
Key Features
- Adaptive Element Tracking: Scrapling can relocate content even after website redesigns using smart similarity algorithms
- Multiple Fetching Methods: HTTP requests with TLS fingerprint impersonation, browser automation, and stealth mode
- Anti-Bot Bypass: Built-in support for bypassing Cloudflare and other anti-bot systems using modified Firefox and fingerprint spoofing
- High Performance: Text extraction benchmarks show ~2ms for 5000 nested elements, significantly faster than many alternatives
- Flexible Selection: CSS selectors, XPath, BeautifulSoup-style find operations, and text-based searching
- Async Support: Full async/await support for concurrent scraping operations
Installation
For basic parsing capabilities:
bash
pip install scraplingFor full features including browser automation:
bash
pip install "scrapling[fetchers]"
scrapling installFor everything including AI features:
bash
pip install "scrapling[all]"
scrapling installBasic Usage
Scrapling uses class methods for HTTP requests:
python
from scrapling import Fetcher
# GET request
response = Fetcher.get("https://example.com")
# POST request with data
response = Fetcher.post("https://example.com/api", data={"key": "value"})
# Access response
print(response.status) # HTTP status code
print(response.body) # Raw bytes
print(response.body.decode()) # Decoded textWhat is CapSolver?
CapSolver is a captcha solving service that uses advanced AI to automatically solve various types of captchas. It provides a simple API that integrates seamlessly with any programming language or scraping framework.
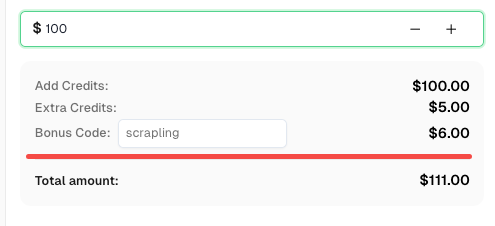
Boost your automation budget instantly!
Use bonus code SCRAPLING when topping up your CapSolver account to get an extra 6% bonus on every recharge — specially for Scrapling integration users.
Redeem it now in your CapSolver Dashboard
Supported Captcha Types
- ReCaptcha v2 (checkbox and invisible)
- ReCaptcha v3 (score-based)
- ReCaptcha Enterprise (both v2 and v3)
- Cloudflare Turnstile
- AWS WAF Captcha
- And many more...
Getting Your API Key
- Sign up at CapSolver
- Navigate to your dashboard
- Copy your API key from the account settings
- Add funds to your account (pay-per-solve pricing)
API Endpoints
CapSolver uses two main endpoints:
- Create Task:
POST https://api.capsolver.com/createTask - Get Results:
POST https://api.capsolver.com/getTaskResult
Setting Up the CapSolver Helper Function
Before diving into specific captcha types, let's create a reusable helper function that handles the CapSolver API workflow:
python
import requests
import time
CAPSOLVER_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY"
def solve_captcha(task_type, website_url, website_key, **kwargs):
"""
Generic captcha solver using CapSolver API.
Args:
task_type: The type of captcha task (e.g., "ReCaptchaV2TaskProxyLess")
website_url: The URL of the page with the captcha
website_key: The site key for the captcha
**kwargs: Additional parameters specific to the captcha type
Returns:
dict: The solution containing the token and other data
"""
payload = {
"clientKey": CAPSOLVER_API_KEY,
"task": {
"type": task_type,
"websiteURL": website_url,
"websiteKey": website_key,
**kwargs
}
}
# Create the task
response = requests.post(
"https://api.capsolver.com/createTask",
json=payload
)
result = response.json()
if result.get("errorId") != 0:
raise Exception(f"Task creation failed: {result.get('errorDescription')}")
task_id = result.get("taskId")
print(f"Task created: {task_id}")
# Poll for the result
max_attempts = 60 # Maximum 2 minutes of polling
for attempt in range(max_attempts):
time.sleep(2)
response = requests.post(
"https://api.capsolver.com/getTaskResult",
json={
"clientKey": CAPSOLVER_API_KEY,
"taskId": task_id
}
)
result = response.json()
if result.get("status") == "ready":
print(f"Captcha solved in {(attempt + 1) * 2} seconds")
return result.get("solution")
if result.get("errorId") != 0:
raise Exception(f"Error: {result.get('errorDescription')}")
print(f"Waiting... (attempt {attempt + 1})")
raise Exception("Timeout: Captcha solving took too long")This function handles the complete workflow: creating a task, polling for results, and returning the solution. We'll use it throughout the rest of this guide.
Solving ReCaptcha v2 with Scrapling + CapSolver
ReCaptcha v2 is the classic "I'm not a robot" checkbox captcha. When triggered, it may ask users to identify objects in images (traffic lights, crosswalks, etc.). For scrapers, we need to solve this programmatically.
How ReCaptcha v2 Works
- The website loads a ReCaptcha script with a unique site key
- When submitted, the script generates a g-recaptcha-response token
- The website sends this token to Google for verification
- Google confirms whether the captcha was solved correctly
Finding the Site Key
The site key is usually found in the page HTML:
html
<div class="g-recaptcha" data-sitekey="6LcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxABCD"></div>Or in a script tag:
html
<script src="https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api.js?render=6LcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxABCD"></script>Implementation
python
from scrapling import Fetcher
def scrape_with_recaptcha_v2(target_url, site_key, form_url=None):
"""
Scrape a page protected by ReCaptcha v2.
Args:
target_url: The URL of the page with the captcha
site_key: The ReCaptcha site key
form_url: The URL to submit the form to (defaults to target_url)
Returns:
The response from the protected page
"""
# Solve the captcha using CapSolver
print("Solving ReCaptcha v2...")
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV2TaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key
)
captcha_token = solution["gRecaptchaResponse"]
print(f"Got token: {captcha_token[:50]}...")
# Submit the form with the captcha token using Scrapling
# Note: Use Fetcher.post() as a class method (not instance method)
submit_url = form_url or target_url
response = Fetcher.post(
submit_url,
data={
"g-recaptcha-response": captcha_token,
# Add any other form fields required by the website
}
)
return response
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = "https://example.com/protected-page"
site_key = "6LcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxABCD"
result = scrape_with_recaptcha_v2(url, site_key)
print(f"Status: {result.status}")
print(f"Content length: {len(result.body)}") # Use .body for raw bytesReCaptcha v2 Invisible
For invisible ReCaptcha v2 (no checkbox, triggered on form submission), add the isInvisible parameter:
python
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV2TaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
isInvisible=True
)Enterprise Version
For ReCaptcha v2 Enterprise, use a different task type:
python
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV2EnterpriseTaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
enterprisePayload={
"s": "payload_s_value_if_needed"
}
)Solving ReCaptcha v3 with Scrapling + CapSolver
ReCaptcha v3 is different from v2 — it runs invisibly in the background and assigns a score (0.0 to 1.0) based on user behavior. A score closer to 1.0 indicates likely human activity.
Key Differences from v2
| Aspect | ReCaptcha v2 | ReCaptcha v3 |
|---|---|---|
| User Interaction | Checkbox/image challenges | None (invisible) |
| Output | Pass/fail | Score (0.0-1.0) |
| Action Parameter | Not required | Required |
| When to use | Forms, logins | All page loads |
Finding the Action Parameter
The action is specified in the website's JavaScript:
javascript
grecaptcha.execute('6LcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxABCD', {action: 'submit'})Common actions include: submit, login, register, homepage, contact.
Implementation
python
from scrapling import Fetcher
def scrape_with_recaptcha_v3(target_url, site_key, page_action="submit", min_score=0.7):
"""
Scrape a page protected by ReCaptcha v3.
Args:
target_url: The URL of the page with the captcha
site_key: The ReCaptcha site key
page_action: The action parameter (found in grecaptcha.execute)
min_score: Minimum score to request (0.1-0.9)
Returns:
The response from the protected page
"""
print(f"Solving ReCaptcha v3 (action: {page_action})...")
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV3TaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
pageAction=page_action
)
captcha_token = solution["gRecaptchaResponse"]
print(f"Got token with score: {solution.get('score', 'N/A')}")
# Submit the request with the token using Scrapling class method
response = Fetcher.post(
target_url,
data={
"g-recaptcha-response": captcha_token,
},
headers={
"User-Agent": solution.get("userAgent", "Mozilla/5.0")
}
)
return response
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = "https://example.com/api/data"
site_key = "6LcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxABCD"
result = scrape_with_recaptcha_v3(url, site_key, page_action="getData")
print(f"Response: {result.body.decode()[:200]}") # Use .body for contentReCaptcha v3 Enterprise
python
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV3EnterpriseTaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
pageAction=page_action,
enterprisePayload={
"s": "optional_s_parameter"
}
)Solving Cloudflare Turnstile with Scrapling + CapSolver
Cloudflare Turnstile is a newer captcha alternative designed as a "user-friendly, privacy-preserving" replacement for traditional captchas. It's increasingly common on websites using Cloudflare.
Understanding Turnstile
Turnstile comes in three modes:
- Managed: Shows a widget only when needed
- Non-Interactive: Runs without user interaction
- Invisible: Completely invisible to users
The good news? CapSolver handles all three automatically.
Finding the Site Key
Look for Turnstile in the page HTML:
html
<div class="cf-turnstile" data-sitekey="0x4xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"></div>Or in JavaScript:
javascript
turnstile.render('#container', {
sitekey: '0x4xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx',
callback: function(token) { ... }
});Implementation
python
from scrapling import Fetcher
def scrape_with_turnstile(target_url, site_key, action=None, cdata=None):
"""
Scrape a page protected by Cloudflare Turnstile.
Args:
target_url: The URL of the page with the captcha
site_key: The Turnstile site key (starts with 0x4...)
action: Optional action parameter
cdata: Optional cdata parameter
Returns:
The response from the protected page
"""
print("Solving Cloudflare Turnstile...")
# Build metadata if provided
metadata = {}
if action:
metadata["action"] = action
if cdata:
metadata["cdata"] = cdata
task_params = {
"task_type": "AntiTurnstileTaskProxyLess",
"website_url": target_url,
"website_key": site_key,
}
if metadata:
task_params["metadata"] = metadata
solution = solve_captcha(**task_params)
turnstile_token = solution["token"]
user_agent = solution.get("userAgent", "")
print(f"Got Turnstile token: {turnstile_token[:50]}...")
# Submit with the token using Scrapling class method
headers = {}
if user_agent:
headers["User-Agent"] = user_agent
response = Fetcher.post(
target_url,
data={
"cf-turnstile-response": turnstile_token,
},
headers=headers
)
return response
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = "https://example.com/protected"
site_key = "0x4AAAAAAAxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
result = scrape_with_turnstile(url, site_key)
print(f"Success! Got {len(result.body)} bytes") # Use .body for contentTurnstile with Action and CData
Some implementations require additional parameters:
python
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="AntiTurnstileTaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
metadata={
"action": "login",
"cdata": "session_id_or_custom_data"
}
)Using StealthyFetcher for Enhanced Anti-Bot Protection
Sometimes basic HTTP requests aren't enough. Websites may use sophisticated bot detection that checks:
- Browser fingerprints
- JavaScript execution
- Mouse movements and timing
- TLS fingerprints
- Request headers
Scrapling's StealthyFetcher provides browser-level anti-detection by using a real browser engine with stealth modifications.
What is StealthyFetcher?
StealthyFetcher uses a modified Firefox browser with:
- Real browser fingerprints
- JavaScript execution capabilities
- Automatic handling of Cloudflare challenges
- TLS fingerprint spoofing
- Cookie and session management
When to Use StealthyFetcher
| Scenario | Use Fetcher | Use StealthyFetcher |
|---|---|---|
| Simple forms with captcha | Yes | No |
| Heavy JavaScript pages | No | Yes |
| Multiple anti-bot layers | No | Yes |
| Speed is critical | Yes | No |
| Cloudflare Under Attack mode | No | Yes |
Combining StealthyFetcher with CapSolver
Here's how to use both together for maximum effectiveness:
python
from scrapling import StealthyFetcher
import asyncio
async def scrape_with_stealth_and_recaptcha(target_url, site_key, captcha_type="v2"):
"""
Combines StealthyFetcher's anti-bot features with CapSolver for ReCaptcha.
Args:
target_url: The URL to scrape
site_key: The captcha site key
captcha_type: "v2" or "v3"
Returns:
The page content after solving the captcha
"""
# First, solve the captcha using CapSolver
print(f"Solving ReCaptcha {captcha_type}...")
if captcha_type == "v2":
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV2TaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key
)
token = solution["gRecaptchaResponse"]
elif captcha_type == "v3":
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV3TaskProxyLess",
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
pageAction="submit"
)
token = solution["gRecaptchaResponse"]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown captcha type: {captcha_type}")
print(f"Got token: {token[:50]}...")
# Use StealthyFetcher for browser-like behavior
fetcher = StealthyFetcher()
# Navigate to the page
page = await fetcher.async_fetch(target_url)
# Inject the ReCaptcha solution using JavaScript
await page.page.evaluate(f'''() => {{
// Find the g-recaptcha-response field and set its value
let field = document.querySelector('textarea[name="g-recaptcha-response"]');
if (!field) {{
field = document.createElement('textarea');
field.name = "g-recaptcha-response";
field.style.display = "none";
document.body.appendChild(field);
}}
field.value = "{token}";
}}''')
# Find and click the submit button
submit_button = page.css('button[type="submit"], input[type="submit"]')
if submit_button:
await submit_button[0].click()
# Wait for navigation
await page.page.wait_for_load_state('networkidle')
# Get the final page content
content = await page.page.content()
return content
# Synchronous wrapper for easier usage
def scrape_stealth(target_url, site_key, captcha_type="v2"):
"""Synchronous wrapper for the async stealth scraper."""
return asyncio.run(
scrape_with_stealth_and_recaptcha(target_url, site_key, captcha_type)
)
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
url = "https://example.com/highly-protected-page"
site_key = "6LcxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxABCD"
content = scrape_stealth(url, site_key, captcha_type="v2")
print(f"Got {len(content)} bytes of content")Full Example: Multi-Page Scraping with Session
python
from scrapling import StealthyFetcher
import asyncio
class StealthScraper:
"""A scraper that maintains session across multiple pages."""
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.api_key = api_key
self.fetcher = None
async def __aenter__(self):
self.fetcher = StealthyFetcher()
return self
async def __aexit__(self, *args):
if self.fetcher:
await self.fetcher.close()
async def solve_and_access(self, url, site_key, captcha_type="v2"):
"""Solve ReCaptcha and access the page."""
global CAPSOLVER_API_KEY
CAPSOLVER_API_KEY = self.api_key
# Solve the ReCaptcha
task_type = f"ReCaptcha{captcha_type.upper()}TaskProxyLess"
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type=task_type,
website_url=url,
website_key=site_key
)
token = solution["gRecaptchaResponse"]
# Navigate and inject token
page = await self.fetcher.async_fetch(url)
# ... continue with page interaction
return page
# Usage
async def main():
async with StealthScraper("your_api_key") as scraper:
page1 = await scraper.solve_and_access(
"https://example.com/login",
"site_key_here",
"v2"
)
# Session is maintained for subsequent requests
page2 = await scraper.solve_and_access(
"https://example.com/dashboard",
"another_site_key",
"v3"
)
asyncio.run(main())Best Practices & Tips
1. Rate Limiting
Don't hammer websites with requests. Implement delays between requests:
python
import time
import random
def polite_scrape(urls, min_delay=2, max_delay=5):
"""Scrape with random delays to appear more human-like."""
results = []
for url in urls:
result = scrape_page(url)
results.append(result)
# Random delay between requests
delay = random.uniform(min_delay, max_delay)
time.sleep(delay)
return results2. Error Handling
Always handle potential failures gracefully:
python
def robust_solve_captcha(task_type, website_url, website_key, max_retries=3, **kwargs):
"""Solve captcha with automatic retries."""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
return solve_captcha(task_type, website_url, website_key, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Attempt {attempt + 1} failed: {e}")
if attempt < max_retries - 1:
time.sleep(5) # Wait before retry
else:
raise3. Respect robots.txt
Check the website's robots.txt before scraping:
python
from urllib.robotparser import RobotFileParser
def can_scrape(url):
"""Check if scraping is allowed by robots.txt."""
rp = RobotFileParser()
rp.set_url(f"{url}/robots.txt")
rp.read()
return rp.can_fetch("*", url)4. Use Proxies for Scale
When scraping at scale, rotate proxies to avoid IP blocks:
python
# CapSolver supports proxy-enabled tasks
solution = solve_captcha(
task_type="ReCaptchaV2Task", # Note: no "ProxyLess"
website_url=target_url,
website_key=site_key,
proxy="http://user:[email protected]:8080"
)5. Cache Solutions When Possible
Captcha tokens are typically valid for 1-2 minutes. If you need to make multiple requests, reuse the token:
python
import time
class CaptchaCache:
def __init__(self, ttl=120): # 2 minute default TTL
self.cache = {}
self.ttl = ttl
def get_or_solve(self, key, solve_func):
"""Get cached token or solve new one."""
if key in self.cache:
token, timestamp = self.cache[key]
if time.time() - timestamp < self.ttl:
return token
token = solve_func()
self.cache[key] = (token, time.time())
return tokenComparison Tables
Captcha Types Comparison
| Feature | ReCaptcha v2 | ReCaptcha v3 | Cloudflare Turnstile |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Interaction | Checkbox + possible challenge | None | Minimal or none |
| Site Key Format | 6L... |
6L... |
0x4... |
| Response Field | g-recaptcha-response |
g-recaptcha-response |
cf-turnstile-response |
| Action Parameter | No | Yes (required) | Optional |
| Solve Time | 1-10 seconds | 1-10 seconds | 1-20 seconds |
| CapSolver Task | ReCaptchaV2TaskProxyLess |
ReCaptchaV3TaskProxyLess |
AntiTurnstileTaskProxyLess |
Scrapling Fetcher Comparison
| Feature | Fetcher | StealthyFetcher |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very fast | Slower |
| JavaScript Support | No | Yes |
| Browser Fingerprint | None | Real Firefox |
| Memory Usage | Low | Higher |
| Cloudflare Bypass | No | Yes |
| Best For | Simple requests | Complex anti-bot |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How much does CapSolver cost?
Check the CapSolver pricing page for current rates.
Q: How do I find the site key on a webpage?
Search the page source (Ctrl+U) for:
data-sitekeyattributegrecaptcha.executeJavaScript callsrender=parameter in reCaptcha script URLsclass="cf-turnstile"for Turnstile
Q: What if the captcha token expires before I use it?
Tokens typically expire after 1-2 minutes. Solve the captcha as close to form submission as possible. If you get validation errors, solve again with a fresh token.
Q: Can I use CapSolver with async code?
Yes! Wrap the solve function in an async executor:
python
import asyncio
async def async_solve_captcha(*args, **kwargs):
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
return await loop.run_in_executor(
None,
lambda: solve_captcha(*args, **kwargs)
)Q: How do I handle multiple ReCaptchas on one page?
Solve each captcha separately and include all tokens in your submission:
python
# Solve multiple ReCaptchas
solution_v2 = solve_captcha("ReCaptchaV2TaskProxyLess", url, key1)
solution_v3 = solve_captcha("ReCaptchaV3TaskProxyLess", url, key2, pageAction="submit")
# Submit with tokens using Scrapling class method
response = Fetcher.post(url, data={
"g-recaptcha-response": solution_v2["gRecaptchaResponse"],
"g-recaptcha-response-v3": solution_v3["gRecaptchaResponse"],
})Conclusion
Combining Scrapling and CapSolver provides a powerful solution for scraping captcha-protected websites. Here's a quick summary:
- Use Scrapling's Fetcher for simple requests where speed matters
- Use StealthyFetcher when facing sophisticated anti-bot systems
- Use CapSolver to solve ReCaptcha v2, v3, and Cloudflare Turnstile
- Implement best practices like rate limiting, error handling, and proxy rotation
Remember to always scrape responsibly:
- Respect website terms of service
- Don't overload servers with requests
- Use the data ethically
- Consider reaching out to website owners for API access
Ready to start scraping? Get your CapSolver API key at CapSolver and install Scrapling with pip install "scrapling[all]".
Compliance Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. CapSolver is committed to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The use of the CapSolver network for illegal, fraudulent, or abusive activities is strictly prohibited and will be investigated. Our captcha-solving solutions enhance user experience while ensuring 100% compliance in helping solve captcha difficulties during public data crawling. We encourage responsible use of our services. For more information, please visit our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
More
Browser Automation for Developers: Mastering Selenium & CAPTCHA in 2026
Master browser automation for developers with this 2026 guide. Learn Selenium WebDriver Java, Actions Interface, and how to solve CAPTCHA using CapSolver.

Adélia Cruz
02-Mar-2026
PicoClaw Automation: A Guide to Integrating CapSolver API
Learn to integrate CapSolver with PicoClaw for automated CAPTCHA solving on ultra-lightweight $10 edge hardware.

Ethan Collins
26-Feb-2026

How to Solve Captcha in Nanobot with CapSolver
Automate CAPTCHA solving with Nanobot and CapSolver. Use Playwright to solve reCAPTCHA and Cloudflare autonomously.

Ethan Collins
26-Feb-2026
How to Extract Structured Data From Popular Websites
Learn how to extract structured data from popular websites. Discover tools, techniques, and best practices for web scraping and data analysis.

Aloísio Vítor
12-Feb-2026

Data as a Service (DaaS): What It Is and Why It Matters in 2026
Understand Data as a Service (DaaS) in 2026. Explore its benefits, use cases, and how it transforms businesses with real-time insights and scalability.

Emma Foster
12-Feb-2026

How to Fix Common Web Scraping Errors in 2026
Master fixing diverse web scraper errors like 400, 401, 402, 403, 429, 5xx, and Cloudflare 1001 in 2026. Learn advanced strategies for IP rotation, headers, and adaptive rate limiting with CapSolver.

Lucas Mitchell
05-Feb-2026