How to Solve CAPTCHA in BrowserMCP with CapSolver API

Lucas Mitchell
Automation Engineer
29-Aug-2025
Want to make AI browser automation solve Captcha very easy? Let's introducing BrowserMCP today, which is a server for AI-driven browser automation using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It enables automated web navigation, form filling, and interaction with applications via clients like Claude Desktop, Cursor, and VS Code. BrowserMCP supports Puppeteer and extensions to enhance automation workflows. Sites with anti-bot protections often trigger CAPTCHAs, which can interrupt tasks.
CapSolver is an AI-powered CAPTCHA-solving service for reCAPTCHA, Turnstile, and more. Integrating CapSolver with BrowserMCP allows automatic CAPTCHA resolution, ensuring seamless AI-driven browser automation.
This guide walks through setup, a full server example, and best practices for automated web navigation, form handling, and CAPTCHA management.
BrowserMCP Overview & Use Cases
BrowserMCP is a server that facilitates browser automation via the Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing AI applications to automate interactions like navigating websites and filling forms. It supports capabilities such as tool execution for browser tasks and integrates with AI clients for seamless control.
Use Cases
BrowserMCP is ideal for AI-enhanced automation scenarios, including:
- Web Automation: Navigating sites, submitting forms, and extracting data using AI instructions.
- Testing: Automating UI tests in browsers controlled by AI clients like Cursor or VS Code.
- RPA Workflows: Building robotic processes for tasks like data entry or monitoring, integrated with AI for decision-making.
- AI Integration: Enabling tools like Claude Desktop to control browsers for research or content generation.
CAPTCHAs frequently interrupt these tasks on protected sites, necessitating an integrated solving solution.
Why CAPTCHA Solving is Needed
Websites employ CAPTCHAs to prevent automated access, which can halt BrowserMCP sessions during navigation or form submission. These barriers require verification, causing failures in AI-driven automations.
Common CAPTCHA types include:
| CAPTCHA Type | Description |
|---|---|
| reCAPTCHA v2 | Requires users to check a box or select images based on a prompt. |
| reCAPTCHA v3 | Uses a scoring system to assess user behavior, often invisible to users. |
| Cloudflare Turnstile | A privacy-focused CAPTCHA alternative that minimizes user interaction. |
CapSolver's extension auto-solves these, allowing BrowserMCP tools to proceed without manual input.
How to Use CapSolver to Handle CAPTCHAs
CapSolver's browser extension detects and solves CAPTCHAs automatically. Integrate it with BrowserMCP by loading the extension during browser launch and using tools to wait for resolution.
Steps to Integrate CapSolver with BrowserMCP
- Sign Up for CapSolver: Register at CapSolver, add funds, and obtain your API key.
- Download and Configure CapSolver Extension: Download from GitHub v1.16.0, unzip, edit
assets/config.jsto add your API key and setreCaptchaMode: 'token'or any other type of captcha that you want to solve. - Set Up Node.js Environment: Install Node.js (v18+ recommended), then add dependencies like
@modelcontextprotocol/sdkandpuppeteer-extravia npm. - Implement BrowserMCP Server: Use the provided script to create an MCP server with tools for browser control, specifying the extension path in
browser_launch. - Configure Client: Set up in AI clients like Cursor, VS Code, or Claude Desktop per docs and extension docs.
- Run and Automate: Launch the server, connect via client, and use prompts to trigger tasks that handle CAPTCHAs.
CapSolver Config Snippet
In your config.js file for the CapSolver browser extension:
javascript
apiKey: 'YOUR_API_KEY',
reCaptchaMode: 'token',This sets up CapSolver to automatically solve reCAPTCHA and other CAPTCHA types during AI-driven browser automation.
BrowserMCP Server Example & Step-by-Step Guide
The following Node.js script demonstrates a custom BrowserMCP server using Puppeteer and CapSolver. It enables AI-powered browser automation for tasks like:
- Web navigation and form filling
- Clicking buttons and typing input
- Capturing screenshots
- Handling CAPTCHAs automatically
Prerequisites
- Install Node.js (v18+)
- Install required packages:
bash
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk puppeteer-extra- Download and configure CapSolver extension as shown above
- Set up MCP in your AI client (e.g., Cursor
settings.jsonwith MCP server config)
With this setup, your AI can automate websites, interact with forms, scrape data, and bypass CAPTCHA challenges efficiently.
Complete Code Example
javascript
#!/usr/bin/env node
/**
* BrowserMCP Server - Model Context Protocol server for browser automation
* This server provides browser automation capabilities through MCP
* Compatible with Claude Desktop, Cursor, VS Code, and other MCP clients
*/
import { Server } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/index.js';
import { StdioServerTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js';
import {
CallToolRequestSchema,
ErrorCode,
ListToolsRequestSchema,
McpError,
} from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/types.js';
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer-extra';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
import { dirname, join } from 'path';
import fs from 'fs/promises';
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
class BrowserMCPServer {
constructor() {
this.browser = null;
this.page = null;
this.server = new Server(
{
name: 'browsermcp-server',
version: '1.0.0',
},
{
capabilities: {
tools: {},
},
}
);
this.setupToolHandlers();
this.setupErrorHandling();
}
setupErrorHandling() {
this.server.onerror = (error) => {
console.error('[MCP Error]', error);
};
process.on('SIGINT', async () => {
await this.cleanup();
process.exit(0);
});
}
setupToolHandlers() {
// List all available tools
this.server.setRequestHandler(ListToolsRequestSchema, async () => {
return {
tools: [
{
name: 'browser_launch',
description: 'Launch a new browser instance with optional Capsolver extension',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
headless: {
type: 'boolean',
description: 'Run browser in headless mode',
default: false,
},
width: {
type: 'number',
description: 'Browser window width',
default: 1280,
},
height: {
type: 'number',
description: 'Browser window height',
default: 720,
},
extensionPath: {
type: 'string',
description: 'Absolute path to the browser extension directory to load (e.g., CapSolver)',
default: '',
},
},
},
},
{
name: 'browser_navigate',
description: 'Navigate to a specific URL',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
url: {
type: 'string',
description: 'URL to navigate to',
},
waitForSelector: {
type: 'string',
description: 'CSS selector to wait for after navigation',
},
timeout: {
type: 'number',
description: 'Navigation timeout in milliseconds',
default: 30000,
},
},
required: ['url'],
},
},
{
name: 'browser_click',
description: 'Click on an element specified by CSS selector',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
selector: {
type: 'string',
description: 'CSS selector of element to click',
},
waitForNavigation: {
type: 'boolean',
description: 'Wait for navigation after click',
default: false,
},
timeout: {
type: 'number',
description: 'Timeout in milliseconds',
default: 5000,
},
},
required: ['selector'],
},
},
{
name: 'browser_type',
description: 'Type text into an input field',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
selector: {
type: 'string',
description: 'CSS selector of input element',
},
text: {
type: 'string',
description: 'Text to type',
},
clear: {
type: 'boolean',
description: 'Clear field before typing',
default: true,
},
delay: {
type: 'number',
description: 'Delay between keystrokes in milliseconds',
default: 0,
},
},
required: ['selector', 'text'],
},
},
{
name: 'browser_get_text',
description: 'Get text content from an element',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
selector: {
type: 'string',
description: 'CSS selector of element',
},
attribute: {
type: 'string',
description: 'Get attribute value instead of text content',
},
},
required: ['selector'],
},
},
{
name: 'browser_wait_for_selector',
description: 'Wait for an element to appear on the page',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
selector: {
type: 'string',
description: 'CSS selector to wait for',
},
timeout: {
type: 'number',
description: 'Timeout in milliseconds',
default: 30000,
},
visible: {
type: 'boolean',
description: 'Wait for element to be visible',
default: true,
},
},
required: ['selector'],
},
},
{
name: 'browser_screenshot',
description: 'Take a screenshot of the current page',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
selector: {
type: 'string',
description: 'CSS selector to screenshot specific element',
},
filename: {
type: 'string',
description: 'Filename to save screenshot',
default: 'screenshot.png',
},
fullPage: {
type: 'boolean',
description: 'Take full page screenshot',
default: false,
},
},
},
},
{
name: 'browser_evaluate',
description: 'Execute JavaScript code in the browser context',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
code: {
type: 'string',
description: 'JavaScript code to execute',
},
},
required: ['code'],
},
},
{
name: 'browser_close',
description: 'Close the browser instance',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {},
},
},
],
};
});
// Handle tool execution
this.server.setRequestHandler(CallToolRequestSchema, async (request) => {
const { name, arguments: args } = request.params;
try {
switch (name) {
case 'browser_launch':
return await this.launchBrowser(args);
case 'browser_navigate':
return await this.navigate(args);
case 'browser_click':
return await this.click(args);
case 'browser_type':
return await this.type(args);
case 'browser_get_text':
return await this.getText(args);
case 'browser_wait_for_selector':
return await this.waitForSelector(args);
case 'browser_screenshot':
return await this.screenshot(args);
case 'browser_evaluate':
return await this.evaluate(args);
case 'browser_close':
return await this.closeBrowser();
default:
throw new McpError(ErrorCode.MethodNotFound, `Unknown tool: ${name}`);
}
} catch (error) {
throw new McpError(ErrorCode.InternalError, `Tool execution failed: ${error.message}`);
}
});
}
async launchBrowser(args = {}) {
// Detailed logging for debugging
console.log('[MCP] launchBrowser called with args:', args);
const {
headless = false,
width = 1280,
height = 720,
extensionPath = 'Capsolver extension path',
} = args;
let launchArgs = [
'--no-sandbox',
'--disable-setuid-sandbox',
'--disable-dev-shm-usage',
'--disable-accelerated-2d-canvas',
'--no-first-run',
'--no-zygote',
'--disable-gpu',
`--window-size=${width},${height}`,
];
if (extensionPath && extensionPath.trim() !== '') {
console.log('[MCP] Launching browser with extension path:', extensionPath);
try {
// Check if extension folder and manifest exist
const manifestPath = join(extensionPath, 'manifest.json');
await fs.access(manifestPath);
console.log('[MCP] Extension manifest found:', manifestPath);
launchArgs.push(`--disable-extensions-except=${extensionPath}`);
launchArgs.push(`--load-extension=${extensionPath}`);
} catch (err) {
console.error('[MCP ERROR] Extension manifest not found:', err);
}
}
const launchOptions = {
headless,
args: launchArgs,
defaultViewport: {
width,
height,
},
};
console.log('[MCP] Puppeteer launch options:', JSON.stringify(launchOptions, null, 2));
try {
console.log('[MCP] About to launch Puppeteer browser...');
this.browser = await puppeteer.launch(launchOptions);
console.log('[MCP] Browser launched. Creating new page...');
this.page = await this.browser.newPage();
console.log('[MCP] Browser launched and page created.');
} catch (err) {
console.error('[MCP ERROR] Failed to launch browser:', err);
throw err;
}
// Set user agent to avoid detection
await this.page.setUserAgent(
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/121.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
);
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `✅ Browser launched successfully!\n- Headless: ${headless}\n- Viewport: ${width}x${height}\n- Extension: ${extensionPath ? 'Loaded' : 'Not loaded'}`,
},
],
};
}
async navigate(args) {
console.log('[MCP] navigate called with args:', args);
if (!this.page) {
console.error('[MCP ERROR] No page instance found in navigate.');
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { url, waitForSelector, timeout = 30000 } = args;
console.log(`[MCP] Navigating to URL: ${url} with timeout: ${timeout}`);
await this.page.goto(url, { waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded', timeout });
console.log(`[MCP] Navigation to ${url} complete.`);
if (waitForSelector) {
console.log(`[MCP] Waiting for selector: ${waitForSelector}`);
await this.page.waitForSelector(waitForSelector, { timeout: 5000 });
console.log(`[MCP] Selector ${waitForSelector} appeared.`);
}
const title = await this.page.title();
const currentUrl = this.page.url();
console.log(`[MCP] Page title: ${title}, Current URL: ${currentUrl}`);
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `✅ Navigated to: ${currentUrl}\n📄 Page title: ${title}`,
},
],
};
}
async click(args) {
if (!this.page) {
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { selector, waitForNavigation = false, timeout = 5000 } = args;
await this.page.waitForSelector(selector, { timeout });
if (waitForNavigation) {
await Promise.all([
this.page.waitForNavigation({ waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded' }),
this.page.click(selector),
]);
} else {
await this.page.click(selector);
}
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `✅ Clicked element: ${selector}`,
},
],
};
}
async type(args) {
if (!this.page) {
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { selector, text, clear = true, delay = 0 } = args;
await this.page.waitForSelector(selector);
if (clear) {
await this.page.click(selector, { clickCount: 3 });
}
await this.page.type(selector, text, { delay });
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `✅ Typed "${text}" into ${selector}`,
},
],
};
}
async getText(args) {
if (!this.page) {
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { selector, attribute } = args;
await this.page.waitForSelector(selector);
let result;
if (attribute) {
result = await this.page.$eval(selector, (el, attr) => el.getAttribute(attr), attribute);
} else {
result = await this.page.$eval(selector, (el) => el.textContent.trim());
}
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `📝 ${attribute ? `Attribute "${attribute}"` : 'Text'} from ${selector}: ${result}`,
},
],
};
}
async waitForSelector(args) {
if (!this.page) {
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { selector, timeout = 30000, visible = true } = args;
await this.page.waitForSelector(selector, { timeout, visible });
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `✅ Element appeared: ${selector}`,
},
],
};
}
async screenshot(args = {}) {
if (!this.page) {
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { selector, filename = 'screenshot.png', fullPage = false } = args;
const options = {
path: filename,
fullPage,
};
if (selector) {
const element = await this.page.$(selector);
await element.screenshot(options);
} else {
await this.page.screenshot(options);
}
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `📸 Screenshot saved: ${filename}`,
},
],
};
}
async evaluate(args) {
if (!this.page) {
throw new Error('Browser not launched. Use browser_launch first.');
}
const { code } = args;
const result = await this.page.evaluate(code);
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: `🔧 JavaScript executed. Result: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`,
},
],
};
}
async closeBrowser() {
if (this.browser) {
await this.browser.close();
this.browser = null;
this.page = null;
}
return {
content: [
{
type: 'text',
text: '✅ Browser closed successfully',
},
],
};
}
async cleanup() {
if (this.browser) {
await this.browser.close();
}
}
async run() {
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await this.server.connect(transport);
console.error('BrowserMCP Server running on stdio');
}
}
const server = new BrowserMCPServer();
server.run().catch(console.error);⚠️ Heads Up
So far, we’ve only been able to get the BrowserMCP + plugin setup working smoothly inside fingerprint browsers—other browsers may behave differently. Also, keep in mind that depending on the AI model you use, it might try to solve CAPTCHAs by itself, which can sometimes clash with the plugin. Just something to watch out for when you’re testing.
Step-by-Step Explanation
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Import Dependencies | Load MCP SDK, Puppeteer, and Node modules for server setup. |
| 2. Define Server Class | Create BrowserMCPServer with tool handlers for browser actions like launch, navigate, click. |
| 3. Launch Browser | In launchBrowser, load CapSolver extension via extensionPath, set viewport, and create page. |
| 4. Tool Handlers | Implement methods for navigation, clicking, typing, etc., using Puppeteer on the active page. |
| 5. Run Server | Connect to stdio transport and start the MCP server for client connections. |
| 6. Cleanup | Handle browser close on interrupt or via tool. |
Demo Walkthrough
This setup demonstrates CAPTCHA solving on a reCAPTCHA demo site using BrowserMCP:
- Server Launch: Run the Node.js script to start the MCP server.
- Client Configuration: In Cursor/VS Code/Claude Desktop, add MCP server config (e.g., via settings.json with npx command).
- Extension Setup: Install BrowserMCP extension, pin it, and connect the tab.
- Prompt Execution: In the client chat, enter: "Go to https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api2/demo , solve the captcha, submit the form and provide me with the response of the page here". The AI uses tools to launch browser with extension, navigate, wait for solve, submit.
- Auto-Solving: CapSolver extension detects/solves CAPTCHA in 'token' mode.
- Response: The client returns the page response post-submission, confirming success.
FAQ Section
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What types of CAPTCHAs can CapSolver solve? | CapSolver supports reCAPTCHA v2/v3, Cloudflare Turnstile, and more. Refer to the CapSolver documentation for a complete list. |
| How do I handle different CAPTCHA types? | Configure the extension for specific types; use browser_wait_for_selector for custom indicators if needed. |
| What if CapSolver fails to solve the CAPTCHA? | Add timeouts/retries in tools or check console logs. Ensure API key has balance. |
| Can I use CapSolver with other MCP tools? | Yes, the extension works browser-wide; integrate into custom tools via evaluate. |
| Do I need proxies with CapSolver in BrowserMCP? | Proxies aid stealth; add to Puppeteer args or extension config for IP rotation. |
Conclusion
Integrating CapSolver’s browser extension with BrowserMCP makes it super easy to let AI handle CAPTCHAs for you. Instead of interrupting your flow, the automation kicks in automatically—whether you’re running projects in Cursor, VS Code, or Claude Desktop. The setup blends MCP’s protocol with CapSolver’s AI-powered CAPTCHA solver, giving you a reliable, interruption-free experience for your browser workflows.
How to Get Started
- Sign up for CapSolver and grab the extension (works with Chrome and Firefox).
- Set up BrowserMCP following the docs.
- Fire up your AI client and try the sample project—you’ll see CAPTCHAs solved instantly.
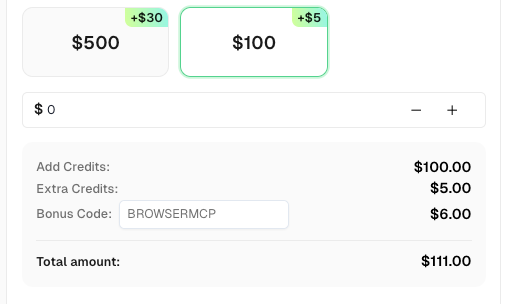
💡 Bonus Tip for BrowserMCP Users: Use the promo code BROWSERMCP when recharging your CapSolver account and get an extra 6% credit. No limits, no expiration—just free bonus credits to keep your automations running.
Supported Browsers and Tools
- BrowserMCP: Runs Chrome/Chromium through Puppeteer; integrates with MCP clients like Claude Desktop, Cursor, VS Code.
- CapSolver: Works as a Chrome/Firefox extension; supports token mode for smooth AI-driven CAPTCHA solving.
Helpful Links
Compliance Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. CapSolver is committed to compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The use of the CapSolver network for illegal, fraudulent, or abusive activities is strictly prohibited and will be investigated. Our captcha-solving solutions enhance user experience while ensuring 100% compliance in helping solve captcha difficulties during public data crawling. We encourage responsible use of our services. For more information, please visit our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
More

How to Solve CAPTCHAs in Python Using Botasaurus and CapSolver (Full Guide)
Learn to integrate Botasaurus (Python web scraping framework) with CapSolver API to automatically solve reCAPTCHA v2/v3 and Turnstile.

Lucas Mitchell
12-Dec-2025

What are 402, 403, 404, and 429 Errors in Web Scraping? A Comprehensive Guide
Master web scraping error handling by understanding what are 402, 403, 404, and 429 errors. Learn how to fix 403 Forbidden, implement rate limiting error 429 solutions, and handle the emerging 402 Payment Required status code.

Sora Fujimoto
11-Dec-2025

Best Web Scraping APIs in 2026: Top Tools Compared & Ranked
Discover the best Web Scraping APIs for 2026. We compare the top tools based on success rate, speed, AI features, and pricing to help you choose the right solution for your data extraction needs.

Ethan Collins
11-Dec-2025

CapSolver Extension: Effortlessly Solve Image Captcha and ImageToText Challenges in Your Browser
Use the CapSolver Chrome Extension for AI-powered, one-click solving of Image Captcha and ImageToText challenges directly in your browser.

Lucas Mitchell
11-Dec-2025

Cloudflare Challenge vs Turnstile: Key Differences and How to Identify Them
nderstand the key differences between Cloudflare Challenge vs Turnstile and learn how to identify them for successful web automation. Get expert tips and a recommended solver.

Lucas Mitchell
10-Dec-2025

How to Solve AWS Captcha / Challenge with PHP: A Comprehensive Guide
A detailed PHP guide to solving AWS WAF CAPTCHA and Challenge for reliable scraping and automation

Rajinder Singh
10-Dec-2025

